Figure 4.
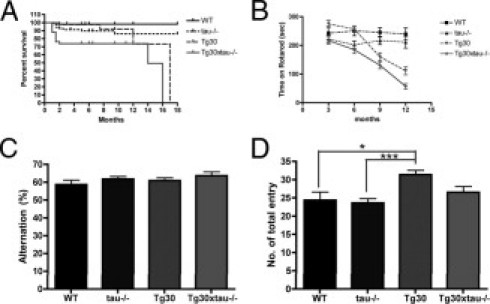
Survival and behavioural analysis of wild-type, tau−/−, Tg30 and Tg30xtau−/− mice. A: Kaplan-Meir survival curves. Tg30xtau−/− mice have a significantly reduced survival by comparison with other genotypes and an accelerated mortality during the first 3 months (P < 0.05, by log-rank test, using pairwise multiple comparison methods) (Bonferroni-corrected threshold method) (n = 178 for four genotypes). B: Rotarod testing. Tg30xtau−/− mice developed a motor deficit starting at 3 months and exhibited a more severe motor deficit than other genotypes (n > 11 for each age, for each genotype). C: Y maze test for alternations at 3 to 6 months. The percentage of alternations was not significantly different among all genotypes (wild-type: n = 11; tau−/−: n = 12; Tg30: n = 15; Tg30xtau−/−: n = 16). D: Number of entries in arms during Y-maze test at 3 to 6 months. The total number of entries was similar among genotypes, except that Tg30 mice had a higher number of entries than wild-type and tau−/− mice. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 by one-way analysis of variance with Bonferonni post hoc tests.
