Figure 5.
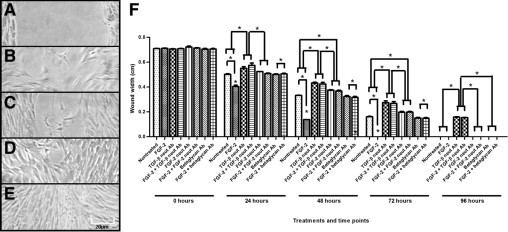
Wound closure of a wounded VIC monolayer, up to 96 hours. Representative phase-contrast micrographs of wounded VICs at 0 (A), 24 (B), 48 (C), 72 (D), and 96 (E) hours. F: Measure of width of the wound, between the two WEs at points of 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours, for various treatments of VICs. Treatment with exogenous FGF-2 resulted in a significantly smaller wound width; therefore, increased wound closure, compared with nontreated VICs, for all points up to complete closure of wounds. Treatment with neutralizing antibody to TGF-β resulted in significantly greater wound width and decreased wound closure compared with nontreated VICs for all points; further addition of FGF-2 in the presence of neutralizing antibody to TGF-β did not yield significantly different results from neutralizing antibody to TGF-β alone for all points. Treatment with neutralizing antibody to FGF-2 resulted in significantly greater wound width and decreased wound closure compared with nontreated VICs for all points up to wound closure, except for 24 hours after wounding; further addition of FGF-2 in the presence of neutralizing antibody to FGF-2 did not yield significantly different results from neutralizing antibody to FGF-2 alone for all points. Treatment with neutralizing antibody to FGF-2 yielded significantly greater wound closure than treatment with neutralizing antibody to TGF-β for all points. Treatment with betaglycan antibody did not result in significantly different wound width compared with nontreated VICs for all points; further addition of FGF-2 in the presence of betaglycan antibody did not yield significantly different results from betaglycan antibody alone for all points. Treatment of FGF-2 in the presence of, individually, neutralizing antibody to TGF-β, neutralizing antibody to FGF-2, or betaglycan antibody resulted in significantly greater wound width and decreased wound closure compared with treatment with FGF-2 alone for all points up to complete closure of wounds. Significance between indicated groups at *P < 0.05, (n = 3).
