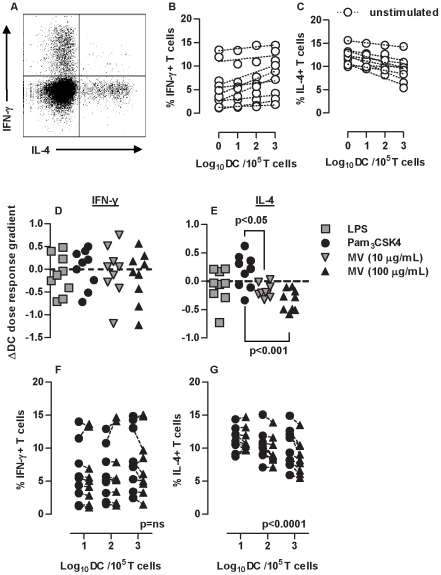
Figure 3. Stimulation of DC with M. vaccae attenuates Th2 responses.
In 3 day allogeneic co-cultures of DC with naive CD4+ T cells, IFN-γ+ and IL-4+ producing T cells were enumerated by intracellular immunofluorescence staining and flow cytometry, after PMA/ionomycin stimulation (A). Increasing DC∶T cell ratios were associated with increased proportions of IFN-γ+ cells, but decreased proportions of IL-4+ cells (p<0.0001, 2-way repeated measure ANOVA) (B–C). In order to assess the effect of DC priming in this model, the regression relationship between DC∶T cell ratio and proportions of IFN-γ+ or IL-4+ cells was determined for each experiment (dotted lines) and the gradient of these relationships in unprimed DC were compared to those of primed DC (D–E). DC priming had no significant effect on DC-dependent IFN-γ polarization of T cells, priming with M. vaccae significantly enhanced DC-dependent reduction of IL-4+ producing T cells in contrast to priming with Pam3CSK4, which had the opposite effect (paired t test). Direct comparison, showed significant reduction (2-way repeated measure ANOVA) of IL-4+ T cells with increasing numbers of DC primed with M. vaccae compared to those primed with Pam3CSK4 (G). No differential effects on IFN-γ+ T cells were evident (F). Data points represent results from individual experiments.