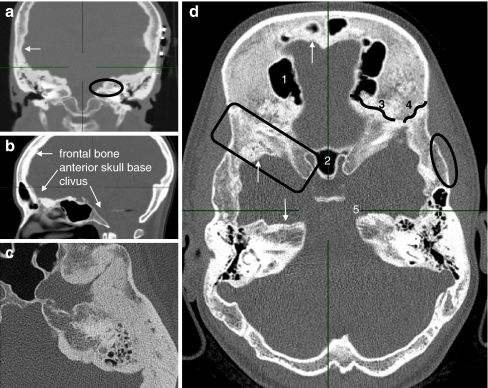
Fig. 1.
CT images of affected individuals. a Coronal reconstruction of the middle skull base with near-total obliteration of the internal auditory canal (oval), endosteally thickened parietal area (arrow). Note the subcutaneous wires of auditory brainstem implantation device (left). b Paramedian sagittal reconstruction. Frontal bone and anterior skull base are affected. Vertebral column, nasal bones and clivus show no hyperostosis. c Axial image of the temporoparietal area revealing exorbitant endosteal hyperostosis. d Axial overview of a 24-year-old affected woman: 1 right frontal sinus, 2 sphenoid sinus, 3 sphenofrontal suture, 4 sphenoparietal suture, 5 apex of the left petrous bone. Arrows apposition of excessive endosteal bone. Oval normal configuration of outer cortex. Square sclerotic greater sphenoid wing