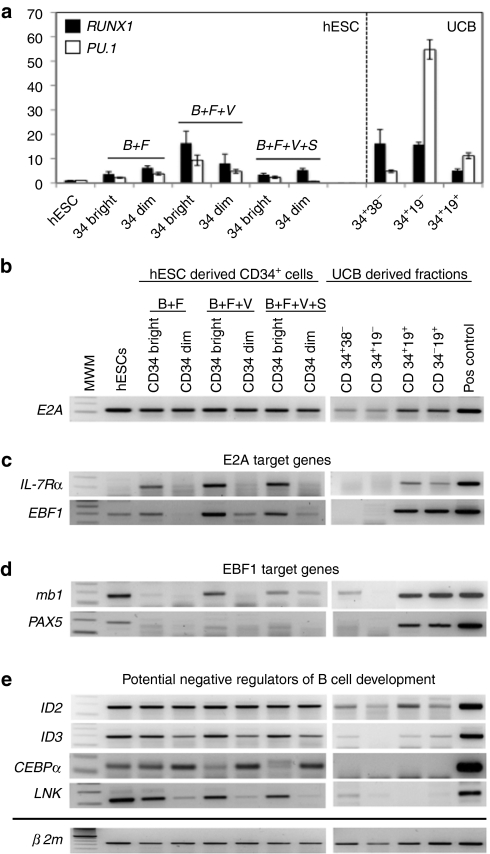
Figure 5.
Gene expression profiles of human embryonic stem cells (hESC)-derived and umbilical cord blood (UCB) CD34+ cell subsets. CD34bright and CD34dim cells were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) from day 8 embryoid bodies (EBs), after generation in three different conditions: (i) bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) (no serum) (B+F), (ii) BMP-4, bFGF, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (no serum) (B+F+V), and (iii) BMP-4, bFGF, and VEGF (+10% serum) (B+F+V+S). (a) Genes involved in early hematopoietic development (RUNX1 and PU.1) were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription (qRT)-PCR in undifferentiated hESC, hESC-derived CD34+ subsets, three CD34+ sub-populations of UCB (CD34+CD38− [containing hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)], CD34+19− (which includes myeloid progenitors) and CD34+CD19+ (B cell progenitors), and mature B cells (CD34-CD19+ cells). Data show mean ± SEM for three independent experiments using H9 cells. Y-axis shows fold change in expression is shown after normalization to housekeeping gene RPL-7. (b–e) Gene expression analysis by semiquantitative RT-PCR using identical cell numbers from each population shown. (b) Expression of E2A, a gene involved in early B cell development. (c) E2A target genes IL-7Rα and EBF1. (d) EBF1 target genes MB-1 and PAX-5. (e) Expression of genes that negatively regulate B cell development. β2 microglobulin (β2M) was used as house keeping gene. Results shown are representative of three independent experiments for each gene analyzed (n = 2; H9 cells, n = 1; H1 cells, n = 3 UCB subfractions).