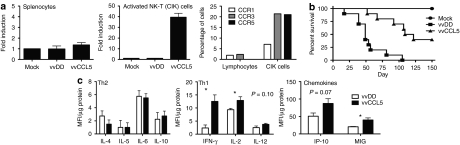
Figure 1.
In vitro chemoattraction of vvCCL5. (a) In vitro chemotaxis of different lymphocyte populations to vvCCL5-infected cells in a transwell assay; (left) bulk unactivated lymphocytes and (centre) cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells; and expression of CCL5 receptors (CCR1, CCR3, and CCR5) on bulk lymphocytes and CIK cells as determined by flow cytometry (representative of three separate experiments, n = 4). (b) Pathogenicity of vvCCL5. Athymic nu−/nu− mice were treated with 1 × 108 plaque forming unit of the different viruses by intraperitoneal injection and subsequent survival followed (n = 10/group). (c) Immune response to vvDD and vvCCL5. C57/BL6 mice treated intraperitoneally with the different viruses (n = 4/group) were euthanized after 4 days and spleens recovered and processed for luminex assay. Relative normalized levels of different cytokines involved in the Th1 or Th2 response and chemokines known to induce a Th1 response are shown. IFN-γ, interferon-γ.