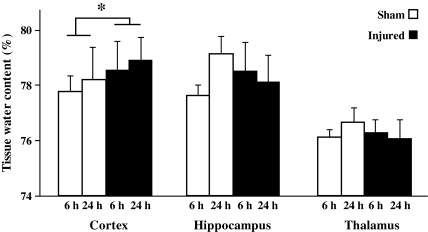
FIG. 8.
Brain edema following concussive brain trauma. Tissue water content was measured in the cortex, hippocampus, and thalamus as described in the methods section. Factorial analysis of variance revealed that brain trauma significantly increased edema in the underlying cortex compared to sham-injured animals over the first 24 h post-surgery/injury. All values are presented as mean±standard deviation (*p<0.05 compared to sham-injured brains).