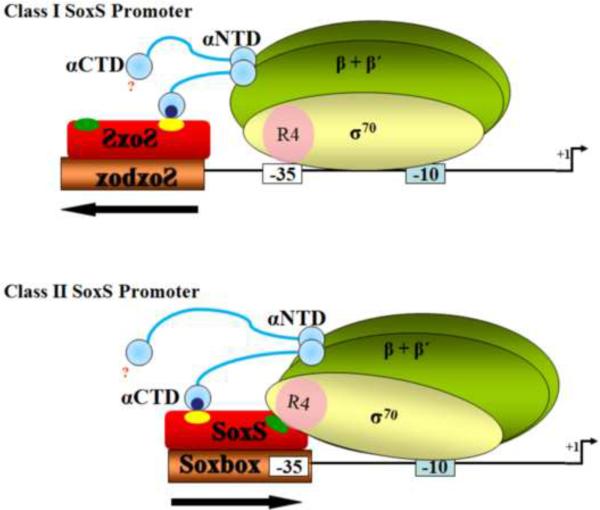
Figure 6.
Cartoon representation of protein-protein interactions at class I and class II SoxS-dependent promoters. The N-terminal and C-terminal domains of the two α subunits, which are connected by a flexible linker, and the β, β' and σ70 subunits of holo-RNAP are labeled and colored as are the −10 and −35 promoter hexamers; the relative position of the start site of transcription is numbered and identified by an arrow. Region 4 and the C-terminal tail of the σ70 subunit are denoted by a pink circle lying within the σ70 subunit and labeled “R4”. SoxS is colored red and the yellow and green circles lying on it represent the class I/II and class II positive control surfaces, respectively53. The soxbox is colored bronze. The backward orientation of SoxS bound to the soxbox and the soxbox itself at canonical class I promoters is denoted by writing “SoxS” from right to left. The protein-protein interactions between the class I/II surface of SoxS and the DNA-binding (265) determinant of the α-CTD55 are denoted by the intersection of the yellow and dark blue circles, respectively. The location of the second α-CTD is unknown and thus is denoted by a question mark. The ability of σ70 R4 to bind to the −35 promoter element of class I promoters and the absence of effects of tri-alanine substitutions on SoxS-dependent transcription activation at these promoters (Table 1) is denoted by the intersection of σ70 R4 (a pink circle) and the promoter hexamer (a colorless rectangle). At canonical class II promoters, the binding of SoxS to the soxbox prevents amino acid residues within σ70 R4 from binding to the −35 region (Table 1). However, amino acid residues within the distal end of R4 and the C-terminal end of σ70 make specific contacts with amino acids within the class I/II surface of SoxS56. For clarity, the interaction between the class II surface of SoxS (colored green) and the amino acids σ70 R4 with which it interacts are not positioned accurately.