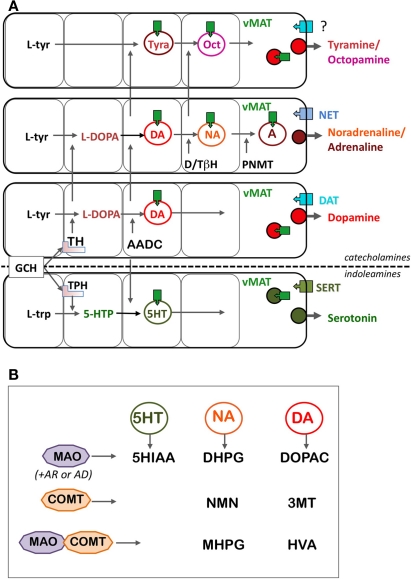
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the metabolic (A) and catabolic (B) pathways of DA and other monoamines. (A) The biosynthesis of DA is highly modular and shares several molecular components with biosynthetic pathways of other monoamines. Catecholamines are synthesized from the aromatic amino acid l-tyrosine, and indoleamines synthesized from the aromatic amino acid l-tryptophan, but TH and TPH display many common characteristics, including the same co-factor (tetrahydrobiopterin, pinkish square under TH and TPH). Tyramine and octopamine come from the same pathways than the other catecholamines, without the primary action of TH. Then, AADC and vMAT are components shared by all the pathways, including indoleamines. Finally, the membrane transporters, DAT, NET, and SERT, responsible for the re-uptake of the monoamines are more specific of the different monoamine pathways based on their cell-expression pattern, although their functional specificity is weak, especially for the DAT and NET (see text). (B) The catabolic enzymes are also essentially shared by all the monoamines. MAO is an intracellular enzyme, whose direct metabolites are rapidly transformed by aldehyde reductases (AR) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (AD) in compounds (5HIAA for serotonin, DHPG for noradrenaline, and DOPAC for dopamine) easy to assay and which reflect the utilization of the transmitters. The effect of COMT, combined to that of MAO, provides metabolites assayable in body fluid such as CSF, blood, or urine, reflecting preferentially the utilization of monoamines at the periphery of the body. Abbreviations: 3MT, 3-methoxytyramine; 5HIAA, 5-hydroxy-acetic acid; 5-HTP, 5-hydroxytryptophan; AADC, aromatic amino acid decarboxylase; AD, aldehyde dehydrogenase; AR, aldehyde reductase; COMT, catechol-O-methyl transferase; DAT, dopamine transporter; DHPG, 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-ethylene-glycol; DOPAC, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate; D/TβH, dopamine/tyramine β-hydroxylase; GCH, GTP cyclohydrolase; HVA, homovanillic acid; l-trp, l-tryptophan; l-tyr, l-tyrosine; MAO, monoamine oxidase; MHPG, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl-ethylene-glycol; NET, noradrenaline transporter; NMN, normetanephrine; Oct, octopamine; PNMT, phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase; SERT, serotonine transporter; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; Tyra, tyramine; vMAT, vesicular monoamine transporter.