Figure 5.
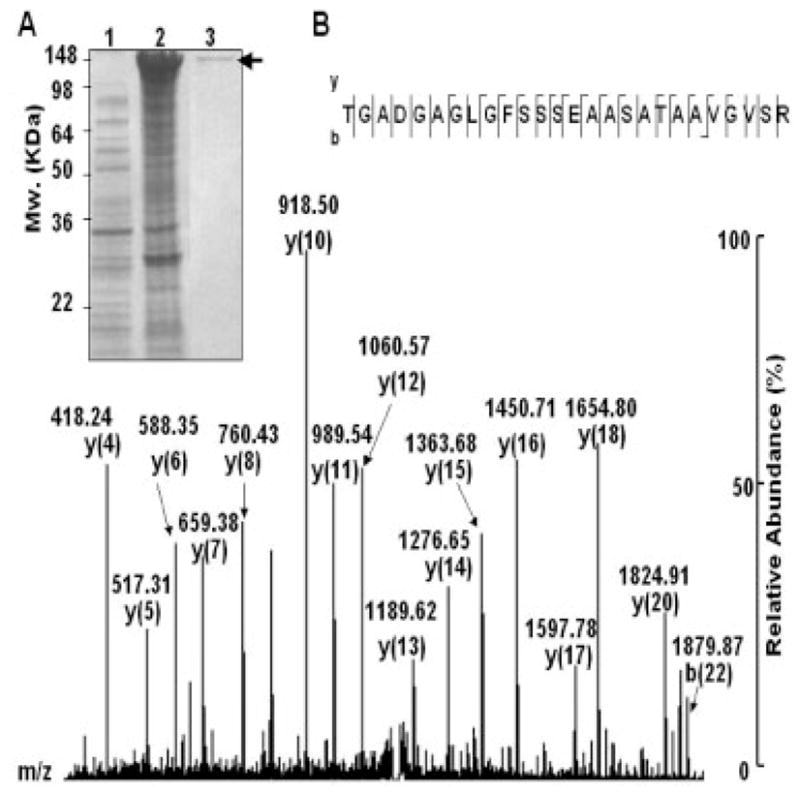
Expression and confirmation of SLP. A vector encoding SLP was constructed by inserting PCR products of SLP into the pEcoli-Nterm 6xHN vector containing a T7/LacO promoter to control protein expression as described in Section 2. The vector with SLP insertion was then transfected into E. coli BL21 (DE3) to construct an E. coli vector-based carrier [E. coli BL21 (DE3) T7/lacO SLP]. For protein expression, E. coli BL21 (DE3) T7/lacO SLP was induced with (A, lane 2) or without (A, lane 1) 1 mM IPTG. SLP-6xNH fusion protein with an approximately 142-kDa molecular weight was overexpressed and detected on a 10% SDS-PAGE. A SLP-6xNH fusion protein was obtained from the elution of a TALON resin column (A, lane 3, arrow). The expression of SLP was confirmed by NanoLC-MS/MS analysis. An internal peptide (TGADGAGLGFSSSEAASATAAVGVSR) of SLP is illustrated (B). The characteristic “y” and “b” series ions were indicated in a MS/MS spectrum.
