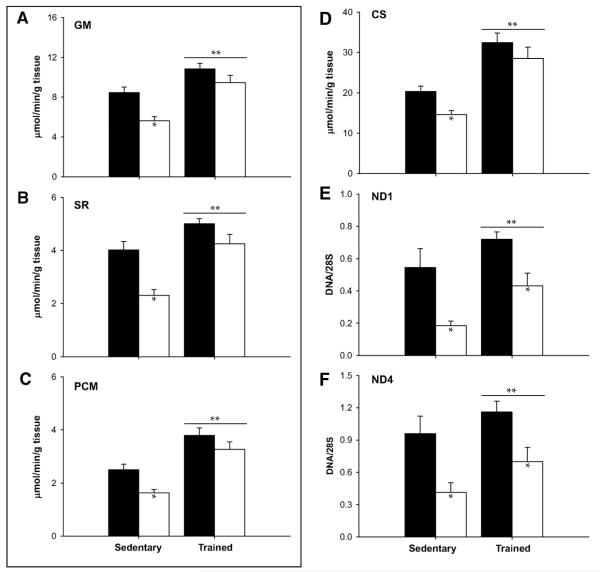
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial ATP production rates were decreased in sedentary older compared to young subjects, but were similar in highly endurance trained young and older adults using substrates glutamate + malate (GM, panel A), succinate + rotenone (SR, panel B), and palmitoyl-l-carnitine + malate (PCM, panel C). Similar results were observed for citrate synthase activity (panel D). Mitochondrial DNA copy number corresponding to NADH dehydrogenase subunits 1 (panel E) and 4 (panel F) were lower in sedentary older adults. Endurance exercise increased mtDNA copy number in both age groups, but could not resolve the age-related decrement. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *Pairwise comparisons revealed significant (P < 0.05) effects of age within activity groups; **significant (P < 0.05) main effects of training. ■, young; □, older. Reproduced with permission from Lanza et al., Diabetes, 2008.