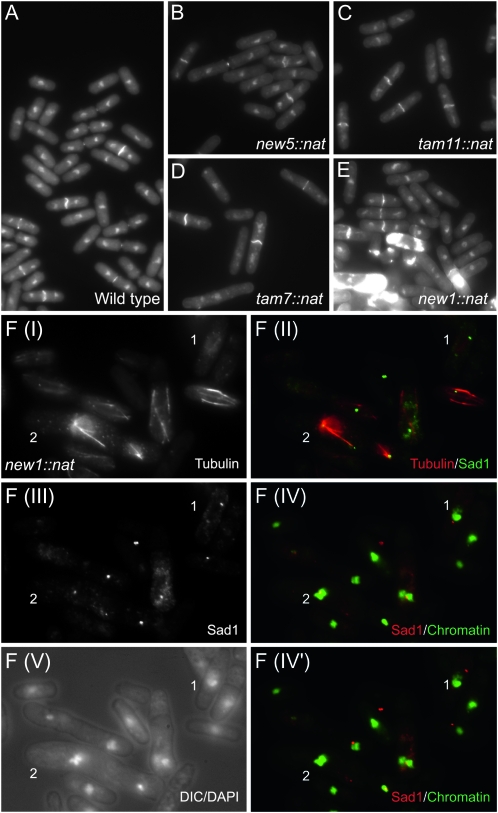
Figure 4.—
Phenotypic characterization of knockout strains. (A–E) Calcofluor DAPI staining of the indicated strains. S. pombe cells grow by linear extension until they reach a critical size threshold. Nuclear division is then initiated, followed by the contraction of the cytokinetic F-actin ring, resulting in separation of the two cytoplasms of the incipient daughter cells. F-actin ring contraction is coupled with the deposition of the cell-wall material of the primary septum that stains strongly as a white bar across the cell equator between the separated nuclei (Marks and Hyams 1985). This primary septum is subsequently degraded to separate the two daughter cells. Thus, the length of cells with the transecting bright calcofluor-positive stain is a direct indication of the timing at which cells commit to mitosis (Nurse 1975). It is clear from B–D that the cells with this bright bar in strains new5.Δ, tam11.Δ, and tam7.Δ are longer than the wild-type controls in A and so are delayed in division. (E) The accumulation of excessive regions of calcofluor staining in new1.Δ cells is indicative of severe defects in septation in some cells in the culture. (F) Anti-tubulin, anti-Sad1 immunofluorescence of new1.Δ cells. DAPI staining of chromatin either alone or in combination with differential interference contrast imaging visualizes the position of the chromatin relative to the cell periphery, as indicated on each panel in the figure. A range of mitotic defects was apparent, including, most notably, a failure in chromosome segregation along elongating spindles (cell 1) and the formation of monopolar spindles with expansive arrays of red microtubules extending from single green foci of Sad1 staining [cell 2: F(II)]. Highly condensed, unsegregated chromosomes cluster around these Sad1 foci [cell 2: F(IV)]. F(IV) and F(IV′) show the same DAPI images of chromatin merged with two different focal planes in the Sad1 channel because the different spindle pole bodies (SPBs) in cells 1 and 2 reside in different focal planes.