Figure 4.
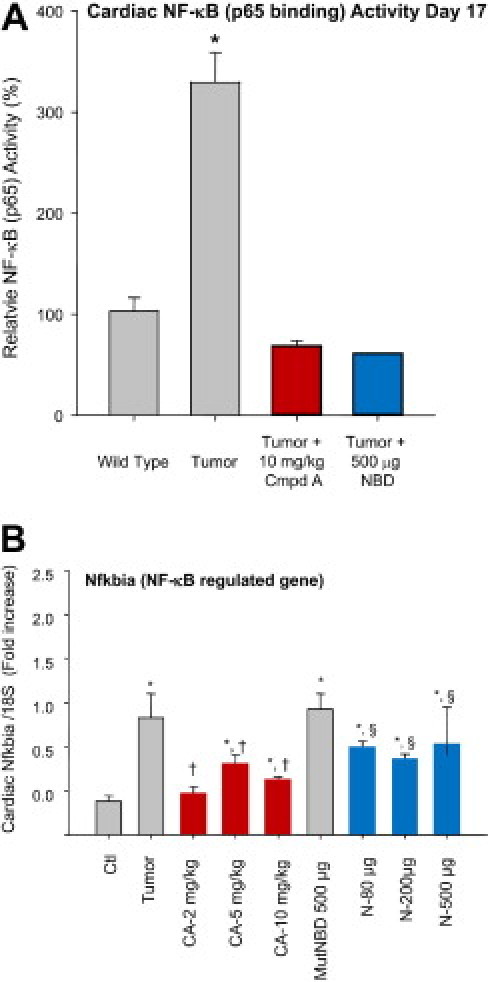
Compound A and NBD peptide inhibit cardiac NF-κB activity. A: NF-κB activity was determined by assaying cardiac nuclear extracts for the ability to bind NF-κB response elements using an ELISA-based assay, and identifying p65 binding (see Materials and Methods for details). At day 17, tumor-induced increases in NF-κB are inhibited significantly by Compound A (10 mg/kg) and the NBD peptide (500 μg). *P < 0.02 versus all other groups. n = 4/group. B: Compound A (CA) and NBD peptide treatment reduced cardiac NF-κB mRNA after 11 days of treatment (day 17). *P < 0.05 versus Ctrl; †P < 0.05 versus Tumor; and §P < 0.05 versus Mut NBD Peptide. n = 3/group. A one-way analysis of variance was performed to determine significance, followed by a multiple comparison procedure (Holm-Sidak method) to determine significance between groups.
