Figure 1.
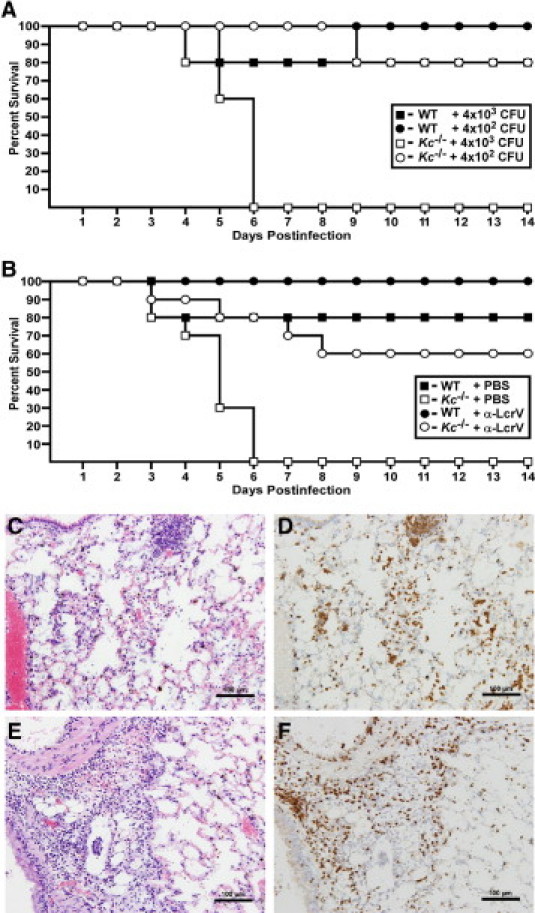
KC contributes to protection against pneumonic plague. A: Wild-type (WT) (n = 5) or Kc−/− C3H mice (n = 5) were challenged by intranasal infection with the indicated doses of Y. pestis CO92 and survival was monitored for 14 days. B: Mice were given 400 μg anti-LcrV polyclonal antibody (n = 3 for wild type; n = 5 for Kc−/−) or PBS (n = 5 for wild type; n = 5 for Kc−/−) by intraperitoneal injection 60 minutes before intranasal challenge with Y. pestis CO92 and survival was monitored for a 14-day period. Data shown were collected in one of two independent experiments with equivalent challenge doses and similar results (n = 10 Kc−/− mice were analyzed for treated and untreated groups). Lungs from moribund mice were inflated with 10% formalin and fixed for 48 hours before staining with H&E (C and E) or anti-Gr-1 (D and F). Both wild-type (C and D) and Kc−/− (E and F) mice developed acute bronchopneumonia with infiltration of neutrophils. Representative images are shown at 20× magnification.
