Figure 6.
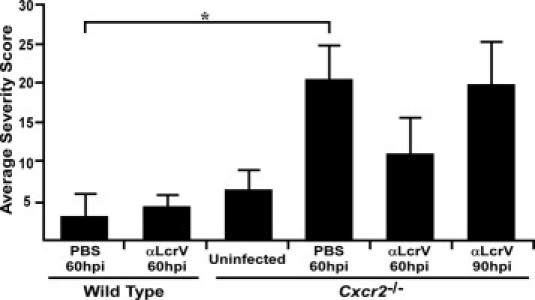
Quantitative histochemistry shows efficient neutrophil recruitment to the lungs of Cxcr2−/− mice despite the failure to prevent bacterial growth and disease. Disease severity scores, based on parenchyml congestion, neutrophil recruitment, edema, and alveolar destruction were determined by analyzing three lung lobes for each mouse and the average score per group was plotted. Group sizes ranged from 2 to 5 [n = 5, uninfected Cxcr2−/−; n = 4 wild type (WT) + PBS, 60 hours; n = 2 WT + anti-LcrV, 60 hours; n = 3 Cxcr2−/− + PBS, 60 hours; n = 3 Cxcr2−/− + anti-LcrV, 60 hours; n = 4 Cxcr2−/− + anti-LcrV, 90 hours]. *P < 0.05 as determined by one-way analysis of variance; hpi indicates hours postinfection.
