Figure 8.
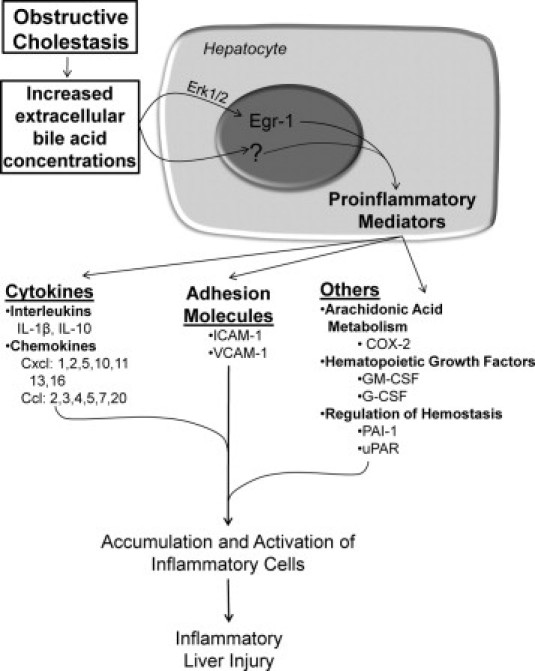
Proposed mechanism of inflammation in the liver during obstructive cholestasis. During obstructive cholestasis, extracellular concentrations of bile acids are increased. Bile acids activate Erk1/2 in hepatocytes which stimulates up-regulation of Egr-1. Egr-1 then regulates production of inflammatory mediators that promote accumulation and activation of inflammatory cells which cause liver injury. Bile acids also up-regulate inflammatory mediators in hepatocytes by an Egr-1-independent mechanism. In addition to hepatocytes, other cell types (not shown) may produce inflammatory mediators that promote inflammatory liver injury during cholestasis.
