Figure 4. Cleavage of Chordin Causes Loss of Dorsalizing and BMP Blocking Activity.
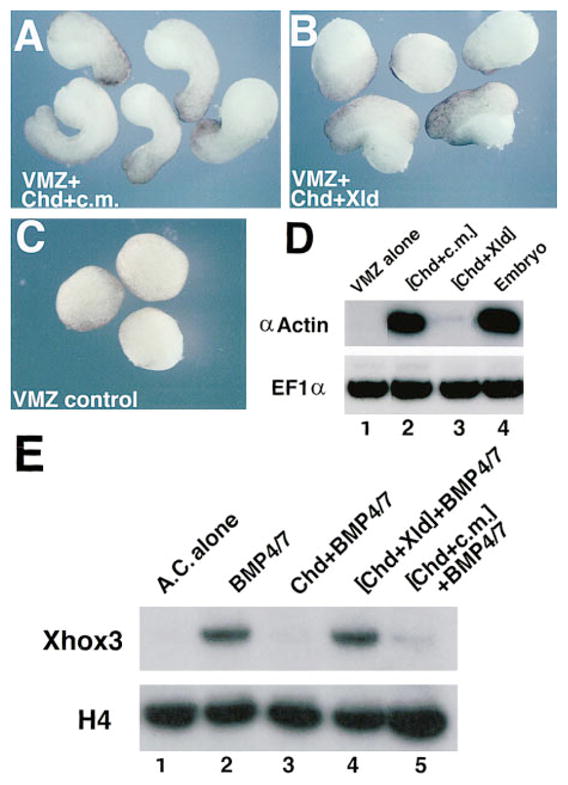
(A–C) External views of ventral marginal zones (VMZs): (A) treated with full-length CHD protein in control medium, (B) treated with XLD-cleaved Chordin protein, and (C) untreated VMZs. Note the lack of elongation in (B).
(D) Dorsal mesoderm is not induced in VMZs treated with digested CHD. RT–PCR analysis was used to score for expression of the muscle-specific marker α-actin in VMZs (n = 20 per lane). EF1α (elongation factor 1α) provides a loading control. Note that digestion with Xolloid inactivates dorsalization by Chordin.
(E) Cleaved CHD is unable to block the activity of BMP-4/7. Animal caps were dissected at blastula stage 8 and incubated with the indicated proteins until siblings reached stage 10̂. Lane 1, untreated animal caps (AC). Lane 2, incubation in 0.7 nM BMP-4/7 induces the ventral mesodermal marker Xhox3. Lanes 3–5, animal caps plus 0.7 nM BMP-4/7 preincubated for 2 hr at 25°C with, respectively, CHD, CHD cleaved by XLD, and CHD incubated in control medium. Note that Chordin preincubated with Xolloid is unable to block BMP signaling.
