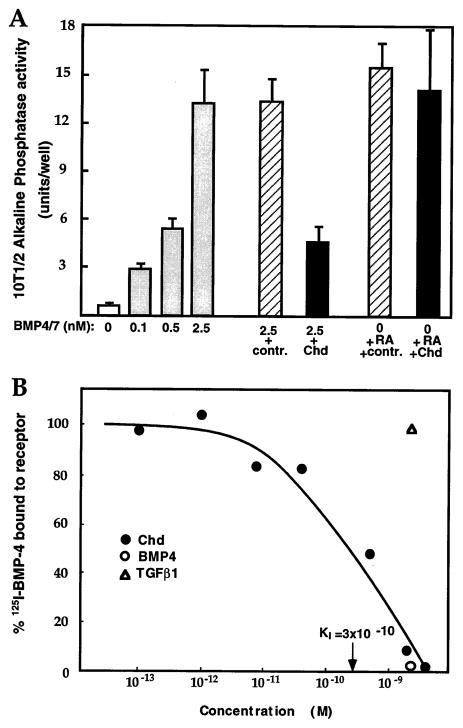
Figure 2. Chordin Protein Inhibits the Osteogenic Activity of Mature BMP Proteins and Prevents Binding to Their Natural Receptors in 10t1/2 Cells.
(A) Dose-dependent induction of alkaline phosphatase in 10t1/2 cells by BMP-4/7 and its inhibition by Chd. Addition of 10 nM Chd reduces the activity of 2.5 nM BMPs to the level induced by 0.5 nM; proteins purified from control-infected cells lacking Chd have no inhibitory activity. Alkaline phosphatase induced by 10−7 M RA is not affected by Chd. Data indicate the mean value of six alkaline phosphatase determinations plus or minus one standard deviation; significance of Chd inhibition is p < 0.001.
(B) Chordin competes binding of 125I–BMP-4 to its natural receptors on 10t1/2 cells. Live cells were incubated with 25 pM 125I–BMP-4 (Massagué, 1987) and competed with increasing concentrations of chordin (closed circles). A 100-fold excess (2.5 nM) of cold BMP-4 (open circle) competed specific binding (leaving 10%–15% background); TGF-β1 did not compete (open triangle). Each data point is the mean of three determinations.