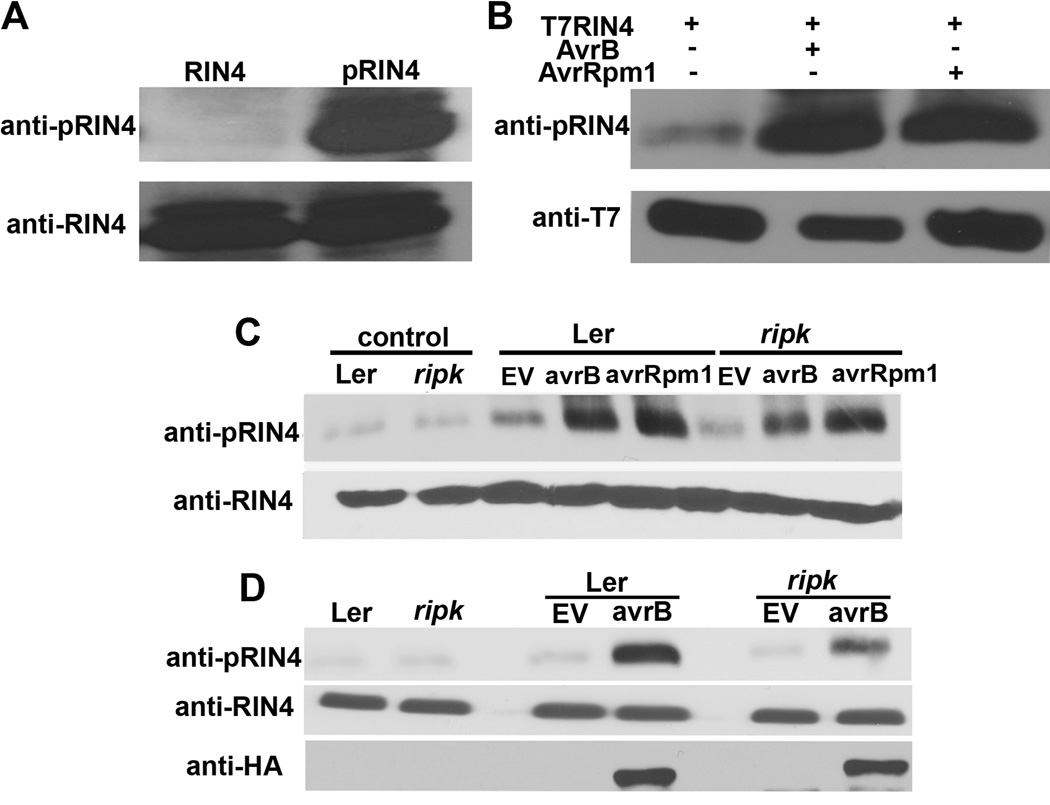
Figure 5. RIN4 phosphorylation is induced by AvrB and AvrRpm1 in vivo.
(A) An antibody raised against a phosphorylated T166 RIN4 peptide (CGADGYpTHIFNK) specifically recognizes phosphorylated RIN4. Lane 1 (RIN4) = recombinant His-RIN4 and MBP-RIPK proteins incubated in the absence of ATP, Lane 2 (pRIN4) = recombinant His-RIN4 and MBP-RIPK proteins incubated in the presence of ATP. Immunoblot analyses with antibodies recognizing phosphorylated RIN4 (anti-pRIN4, upper panel) and RIN4 (anti-RIN4, lower panel). (B) T7-RIN4 phosphorylation in N. benthamiana after co-expression with AvrB or AvrRpm1 using Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression. Protein was extracted from leaf disks 40h post-infiltration and subjected to immunoblot analyses. (C) RIN4 phosphorylation in Arabidopsis Ler and ripk after delivery of AvrB and AvrRpm1. Arabidopsis leaves were infiltrated with 5×107cfu/ml of Pst DC3000 and Pst DC3000(avrB) or (avrRpm1). Immunoblot analysis was performed 6h post-inoculation. Upper panel = phosphorylated RIN4 immunoblot, lower panel = anti-RIN4 immunoblot, control = 0h time point, EV = Pst DC3000 control. (D) AvrB-HA is expressed at similar levels in Ler and ripk plants. Ler and ripk plants were syringe infiltrated with 5×107cfu/ml of Pst DC3000(avrB-HA). Immunoblot analysis was performed 6h post-inoculation. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. See also Figure S4.