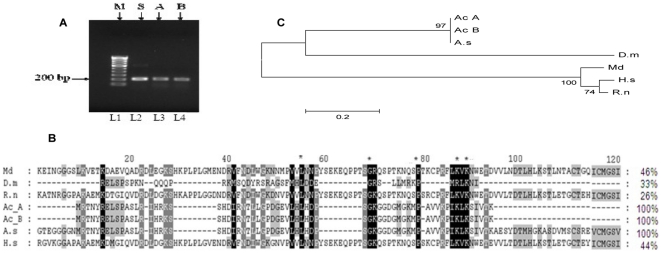
Figure 6. Homology analysis of An. culicifacies sp A and sp B.
(A) PCR amplification of Exon-1 region (200 bp) fragment of mosquito nitric oxide synthase (NOS): L1: 100 bp marker (M); L2: An stephensi (S): L3: An. culicifacies sp A: L4: An. culicifacies sp B. (B) Clustal alignment of AcNOS with known homologus NOS sequence of other insect and vertebrate. Highly conserved and similar residues have been shown dark black & grey respectively. Relative sequences identity has also been shown. (C) Phylogenetic bootstrap consensus tree based on amino acid sequence alignment using Neighbor- joining method. Length of Horizontal lines is proportional to the minimum number of amino acids differences required to join nodes. Numerical numbers in the nodes are bootstrap confidence intervals which were calculated by 1000 heuristic search replicates. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method. Species name and respective sequences accession numbers includes; M. d: Monodelphis domestic (XP_001362705.1); D. m: Drosophila melanogaster (AAF25682.1); R.n: Rattus norvegicus (NP_434686.1); A.c_A: Anopheles culicifacies sp A (FJ172997); A.c_B: Anopheles culicifacies sp B (FJ172998); A.s: Anopheles stephensi (061608.2); H.s: Homo sapiens(NP_000611.1).