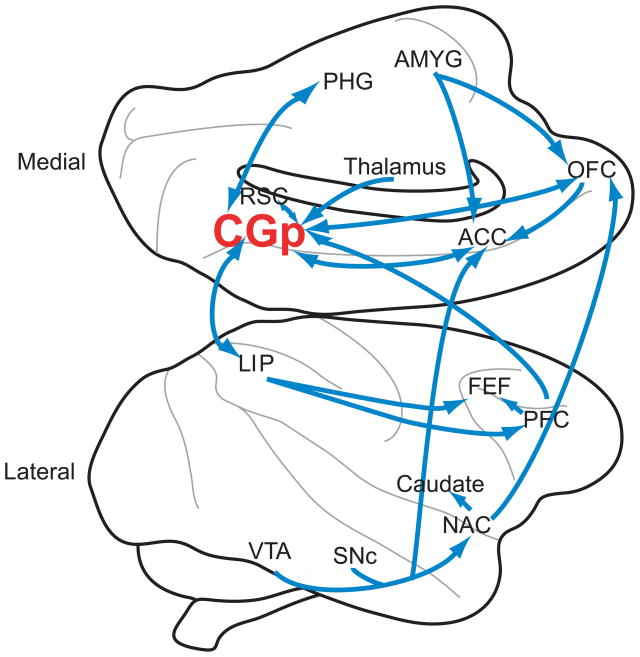
Box 1, Figure I.
Figure shows medial (top) and lateral (bottom) views of the macaque brain. Significant neuroanatomical connections to and from CGp are shown. Note that the figure does not represent a thorough diagramming of innervations, as CGp connects to a large number of brain regions. Generally, CGp neuroanatomy is similar in humans and macaques [73]. Abbreviations: VTA=ventral tegmental area; SNc=Substantia nigra pars compacta; NAC=nucleus accumbens; PFC=prefrontal cortex; FEF=frontal eye field; LIP=lateral intraparietal area; CGp=posterior cingulate cortex; ACC=anterior cingulate cortex; RSC=retrosplenial cortex; PHG=parahippocampal gyrus; OFC=orbitofrontal cortex; AMYG=amygdala