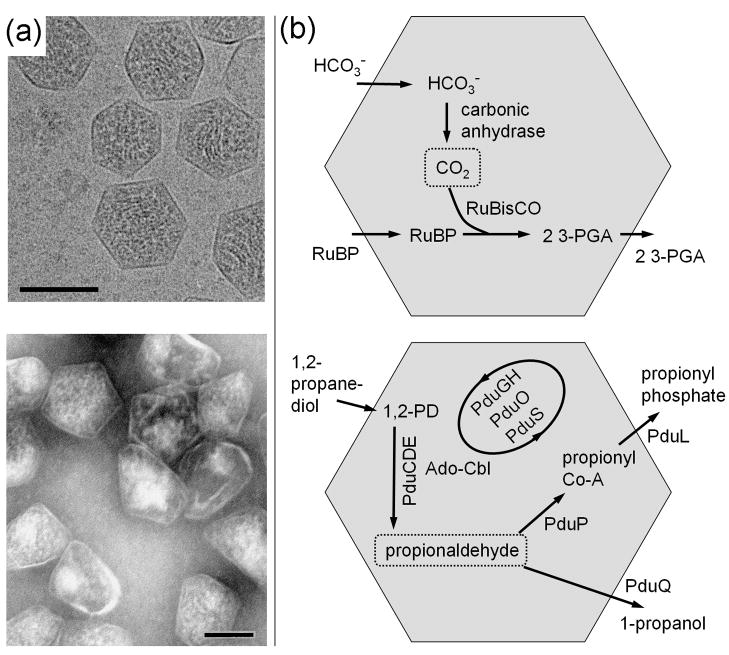
Figure 1.
Examples of bacterial microcompartments. (a) Electron micrographs of purified carboxysomes (top) from Halothiobacillus neapolitanus and purified propanediol utilization (Pdu) microcompartments (bottom) from Salmonella enterica. The scale bars are 100 nm. Under conditions where they are produced, several microcompartments are typically found within each bacterial cell. (b) Diagram of CO2 fixation in the carboxysome (top) and a simplified diagram of propanediol metabolism in the Pdu microcompartment (bottom). RuBP is 1,5-ribulose bisphosphate and 3-PGA is 3-phosphoglycerate. Reactions in the Pdu microcompartment involve multiple cofactors (not shown), including NAD+/NADH, ATP, coenzyme-A, and a B12 cofactor, with reactivation and replacement of the latter cofactor being carried out by the PduGH, PduS, and PduO enzymes. In each microcompartment, the key encapsulated intermediate is boxed. Carboxysomes were provided by Gordon Cannon and Sabine Heinhorst and imaged by Kelly Dryden and Mark Yeager.