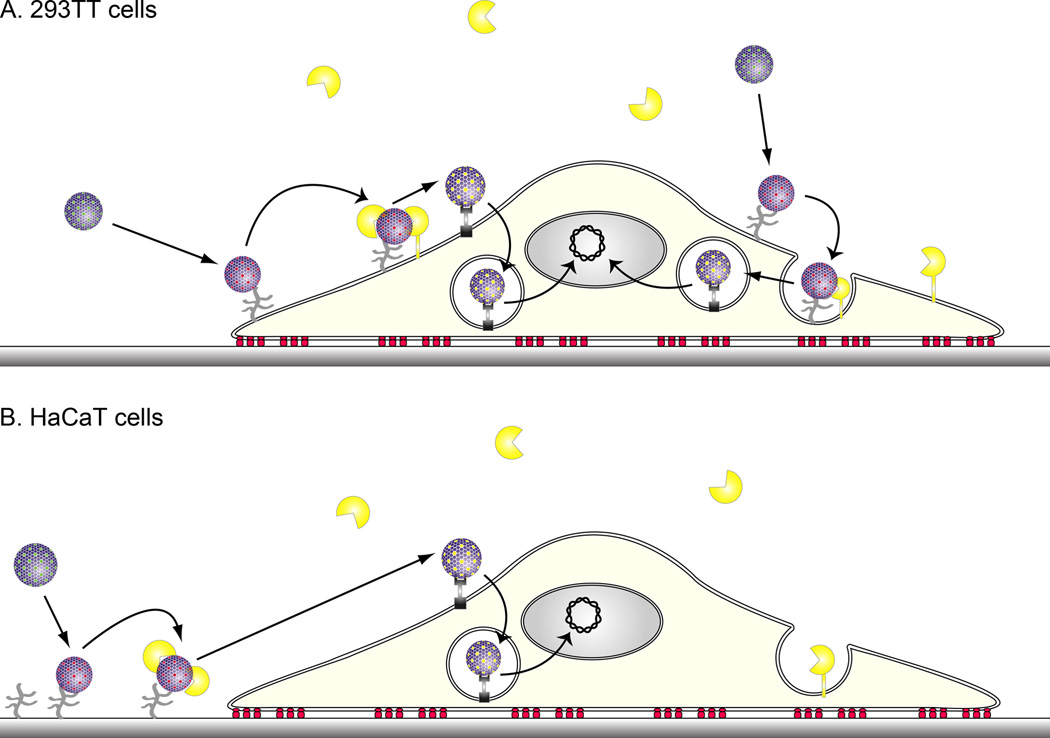
Figure 3. In vitro infection of 293TT and HaCaT cells by HPV.
A. In vitro infection of 293TT cells. Early studies of in vitro infection by HPV utilized 293TT or other transformed cell lines as target cells. HPV binds directly to the 293TT cell surface via HSPGs which triggers a conformational change in the capsid such that the amino terminus minor capsid protein L2 becomes exposed. Exposure of L2 renders it accessible to cleavage by furin [50]. Furin-cleavage of L2 is essential to infection and is associated with escape of L2 and the viral genome from the endosome. γ secretase activity is also required for infection, but it is unclear what it cleaves [51]. The viral genome-L2 complex is too large to cross the nuclear envelope, but gains access to the nucleus as during mitosis while its membrane has dissolved [52]. B. In vitro infection of HaCaT cells or primary keratinocytes. In contrast to 293TT cells, HPV binds first to the laminin-5 associated extracellular matrix via HSPGs secreted upon the culture surface prior to infection of the immortalized keratinocyte line HaCaT or primary keratinocytes. Upon attachment to the extracellular matrix, the HPV virions undergo a conformational shift that exposes L2 for cleavage by secreted furin. Only then can the virions bind to a secondary receptor on the keratinocyte surface for subsequent uptake. Antibodies reacting with particular loops on the capsid surface (e.g. H16.V5 and H16.E70 monoclonal antibodies) can prevent virions binding to the extracellular matrix, but these antibody-bound virions can still bind the cell surface, although infection does not occur. In the presence of antibodies reacting with other surface L1 loops (e.g. H16.U4 monoclonal antibody), the binding of HPV to the basement membrane, and the cleavage of L2 by furin still occurs, but the virions are unable to transfer to the viral receptor on the basal epithelial cells [27]. Likewise, L2-specific antibodies (e.g. RG-1 monoclonal antibody) allow the binding of HPV to the basement membrane, and the exposure of L2. The antibody binds to the exposed L2 after its cleavage by furin and the virions are unable to transfer to the viral receptor on the basal epithelial cells [27].