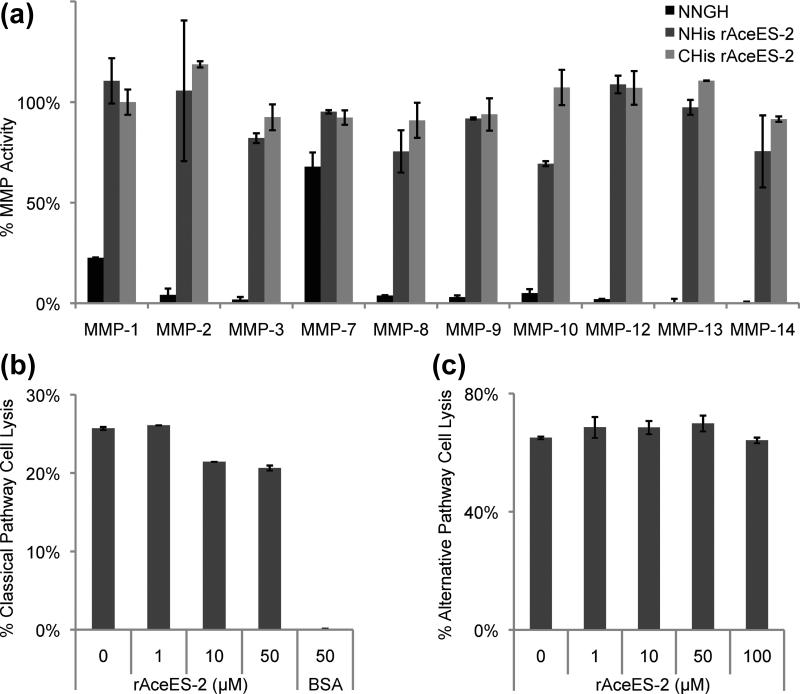
Fig. 4.
MMP activity and complement-mediated cell lysis inhibition assays with rAceES-2. (a) A colorimetric kit was used to test the ability of rAceES-2 to inhibit cleavage of a thiopeptide substrate by human MMPs 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13 and 14 (Enzo Life Sciences). The cleavage product reacts with 5,5’-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) to yield 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoic acid, which can be detected by absorbance at 412 nm. Final MMP concentrations in the reactions were 17-126 nM according the manufacturer's protocol. AceES-2 with either N- or C-terminal histidine tags (NHis and CHis, respectively) do not significantly inhibit any of MMPs tested. Shown is one representative experiment using 2.0 μM rAceES-2, which corresponds to a rAceES-2:MMP molar ratio of between 15:1 and 115:1, depending on the concentration of MMP used. Similar results where obtained using up to 20 μM rAceES-2. The general peptide inhibitor NNGH was used as an inhibitory control. (b) The ability of rAceES-2 to complement pathways was tested using standard erythrocyte lysis assays (see Supplementary Data for detailed methods). rAceES-2 does not significantly inhibit complement-mediated lysis of sheep erythrocytes in the classical pathway relative to a buffer control. Bovine serum albumen (BSA) at 50 μM inhibits this pathway non-specifically. (c) rAceES-2 does not significantly inhibit complement-mediated lysis of rabbit erythrocytes in the alternative pathway.