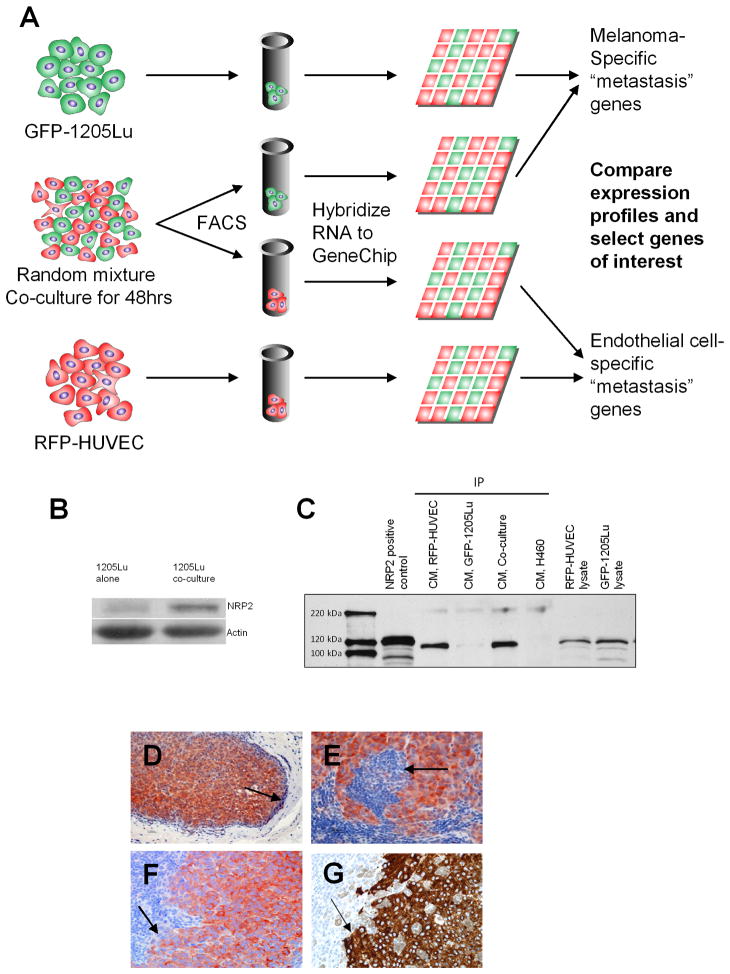
Figure 2. Global Gene Expression Profiling of Melanoma-Endothelial Cell Interactions Identifies Neuropilin-2 as A Mediator of Cellular Communication.
(A) Schematic representation of screen to identify genes involved in melanoma-endothelial cell communication. Populations of RFP-HUVECs and GFP-1205Lu metastatic melanoma cells were plated in a co-culture system (method II) and incubated for 48 hours. Cells were sorted by FACS and RNAs isolated and hybridized to a pan-genomic human GeneChip. Expression profiles altered by co-culture were compared against those in homotypic cultures of RFP-HUVECs and GFP-1205Lu cells to identify genes associated with melanoma-endothelial cell communication.
(B) Western blot for NRP2 expression in GFP-1205Lu cells grown in homotypic cell culture or following heterotypic co-culture with RFP-HUVECs.
(C) IP-Western analysis of NRP2 expression in conditioned medium from RFP-HUVECs, GFP-1205Lu melanoma cells or HUVEC-1205Lu co-cultures. H460 (NRP1+/NRP2−) lung cancer cells are included as a negative control for NRP2. RFP-HUVEC and GFP-1205Lu cell lysates are included as controls for non-secreted expression of NRP2.
(D–F) Immunohistochemical staining for NRP2 in human melanoma metastases at low-power magnification (D) and high-power magnification (E, F). Arrows point to demarcation of tumor-metastatic niche interface.
(G) Melan-A stain for melanoma cells depicted in (F) demonstrating correlation of NRP2 and Melan-A staining in serial tumor sections.