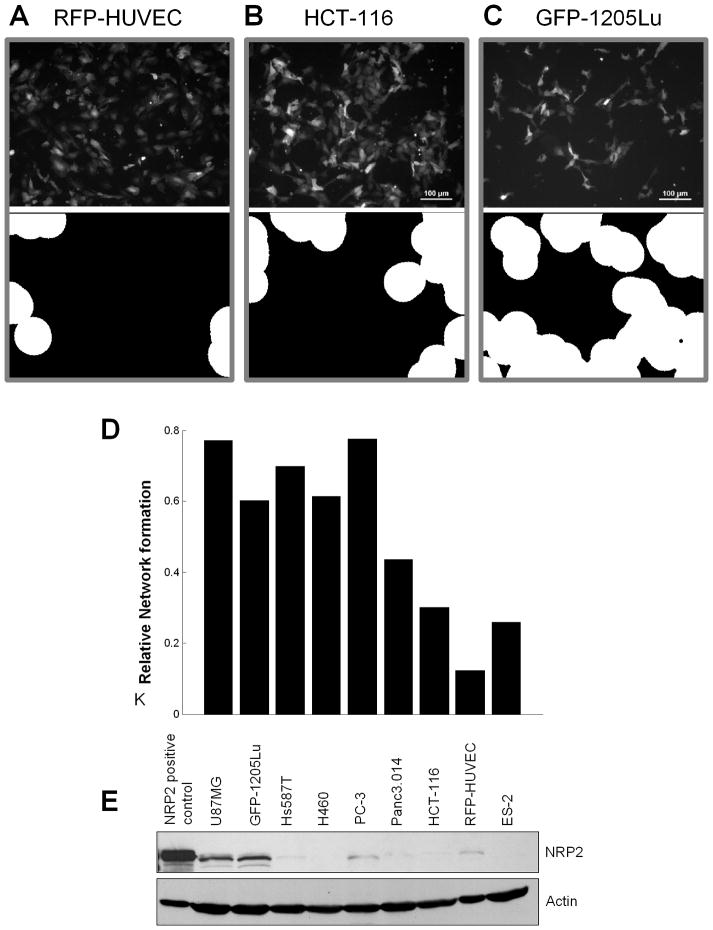
Figure 5. Cell-cell communications with different tumor cell types induces variable degree of HUVECs patterning.
(A–C) Patternings of RFP-HUVECs co-cultured with different tumor cell lines were obtained following 48 hours of co-culture (top panel) and evaluated using the morphological analysis of HUVEC network formation (lower panel) described in Methods for (A) RFP-HUVECs alone, RFP-HUVEC’s co-cultured with HCT-116 colon cancer cells (B), and RFP-HUVECs co-cultured with GFP-1205Lu melanoma cells (C).
(D) Quantification of the morphological analysis of HUVEC patterning induced by co-culture with various tumor cell lines vs. HUVEC alone.
(E) Western blot analysis of NRP2 expression in various tumor cell lines grown in heterotypic co-culture with RFP-HUVECs. The tumor cell lines used were: glioblastoma, U87MG; melanoma, GFP-1205Lu; breast cancer, Hs578T; non-small cell lung carcinoma, H460; prostate cancer, PC-3; pancreatic cancer, Panc3.014; colon cancer, HCT-116; ovarian cancer, ES-2.