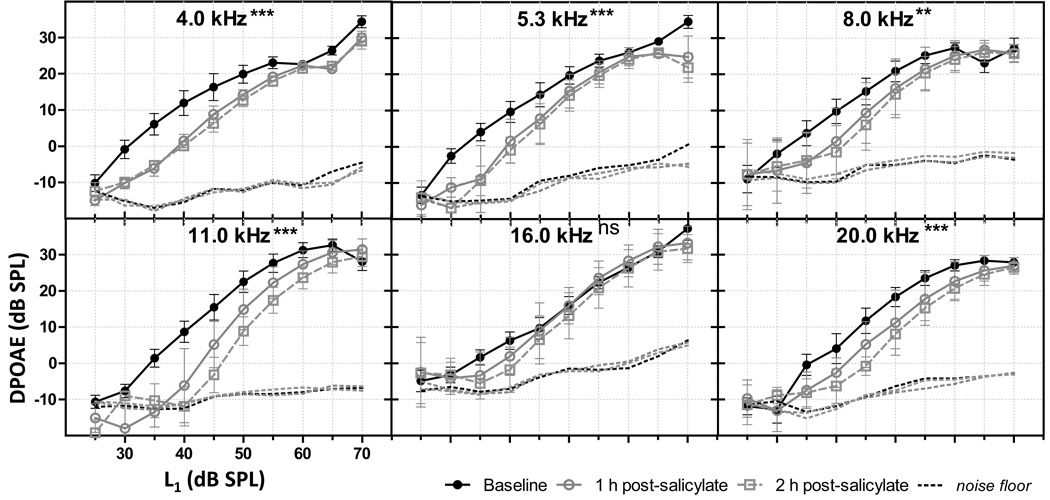
Fig 1.
Salicylate’s effects on DPOAE I/O functions. Acute systemic salicylate administration significantly decreased the DPOAE I/O functions for DP (2•f1-f2) below (4.0, 5.3, 8.0, and 11.0 kHz) and above (20.0 kHz) the tinnitus pitch (16.0 kHz). Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM). (p < 0.05*, p< 0.01**, p < 0.001***, ns = not significant).