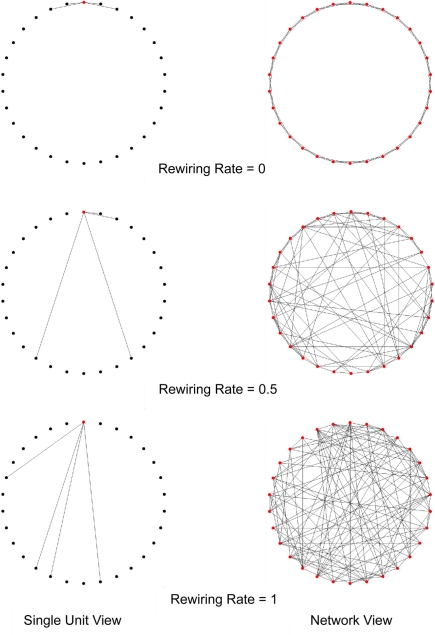
Figure 1.
The rewiring process in a Watts–Strogatz small-world network. In this example, the network contains 30 units and four afferent connections to each unit. Initially all units are locally connected, as p = 0. Then a proportion of connections of each unit are randomly rewired (p = 0.5). As the rewiring rate increases, the network becomes a completely random network (p = 1). Note that the connections are formed on a one dimensional line but are drawn in 2-D figures for better visualization.