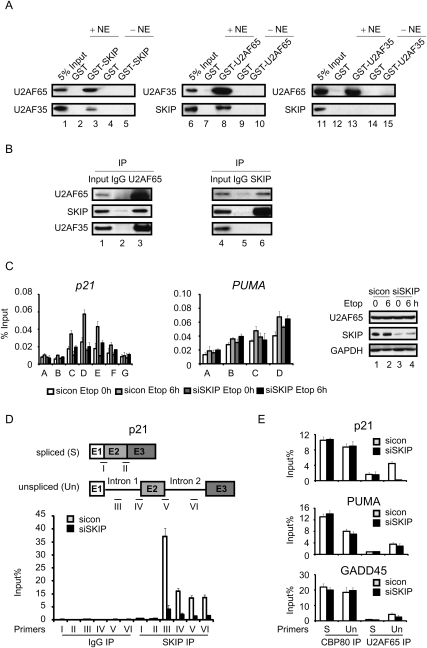
Figure 4.
SKIP associates with unspliced p21 mRNA and recruits U2AF65. (A) Immunoblot analysis of the interaction between SKIP, U2AF35, and U2AF65 in GST pull-down experiments from HCT116 cell nuclear extract. (B) Total proteins were extracted from U2OS cells for coimmunoprecipitation. Immunoprecipitates were examined by Western blot using antibodies against SKIP, U2AF35, or U2AF65. (C) ChIP analysis of U2AF65 binding on the p21 and PUMA genes. U2OS cells were transfected with control or SKIP siRNA for 48 h, followed by treatment with vehicle or etoposide (20 μM) for 6 h. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against U2AF65. ChIP-enriched DNA was quantified by qPCR with the indicated primers in Figure 2A and Supplemental Figure S2A. (Right panel) Immunoblot analysis. Error bars represent the standard deviation obtained from three independent experiments. (D, top panel) Schematic representation of the primer pairs used to detect p21 unspliced and spliced mRNAs. RNA-IP analysis of binding of the SKIP protein to p21 unspliced or spliced mRNA. U2OS cells were transfected with control or SKIP siRNA for 48 h. RNA samples were purified from nonprecipitated cellular lysates (input), or extracts precipitated with control IgG or SKIP antibody. Immunoprecipitated p21 mRNA was detected using qRT–PCR with the indicated primers. Values were expressed as percentage of input RNA. Error bars represent the standard deviation obtained from three independent experiments. (E) RNA-IP analysis of binding of CBP80 or U2AF65 to p21, PUMA, or GADD45 unspliced or spliced mRNA. Experiments were performed as in D. The primers used for detecting p21 transcripts were primer IV (unspliced) and primer I (spliced) as in D. The primers used for detecting PUMA or GADD45 transcripts were the same as in Figure 3B.