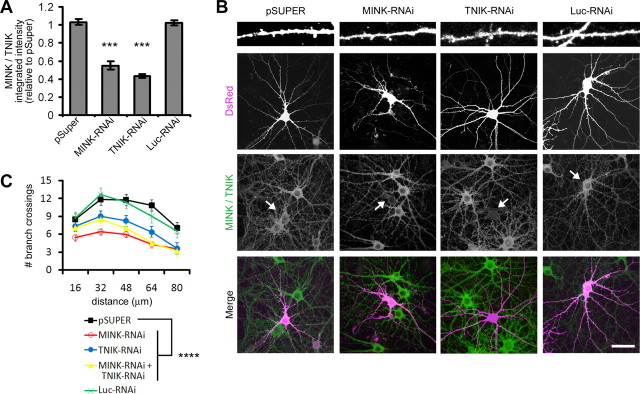
Figure 2.
MINK- and TNIK-RNAi diminish neuronal complexity. A, Mean cell body MINK/TNIK immunostaining intensity for hippocampal neurons transfected with pSuper or pSuper-based RNAi constructs targeting MINK (MINK-RNAi), TNIK (TNIK-RNAi), or luciferase (Luc-RNAi), as indicated. Mean integrated intensity values were normalized to pSuper-transfected neurons. Error bars indicate ±SEM. ***p < 0.001 relative to pSuper control, ANOVA. n ≥ 12 neurons for each. B, Representative images of hippocampal neurons cotransfected with pSuper or RNAi constructs as indicated, along with DsRed to visualize transfected cell morphology. Immunostaining was performed with antibodies to endogenously expressed MINK/TNIK. Arrows indicate transfected neurons. Dendritic segments at top are 40 μm long. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, Sholl analysis, transfections as indicated (n ≥ 12 neurons for each). A significant difference between transfected groups was confirmed by a 5 × 5 mixed-effect ANOVA, with transfected group as the five-level between-group effect and distance from the soma as the five-level within-group effect (F(4,332) = 15.625; p < 0.0001). Post hoc tests (PLSD) revealed that, relative to pSuper control, a loss of either MINK, TNIK, or simultaneous knockdown of MINK and TNIK significantly reduced dendritic complexity (****p < 0.0001).