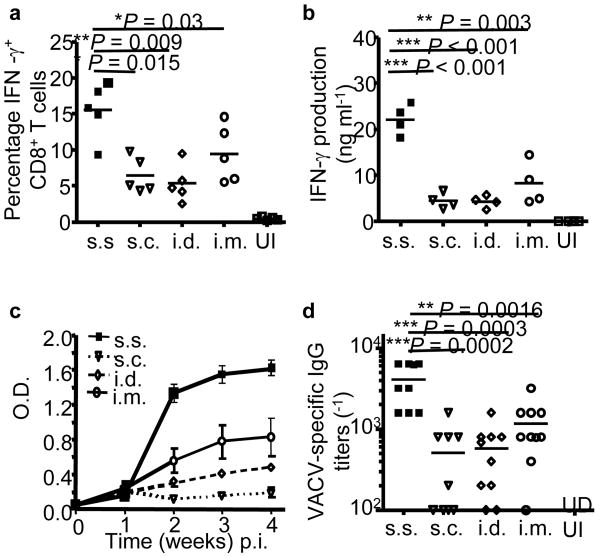
Figure 1. Inoculation with rVACV via barrier-disrupted epidermis generates significantly stronger cellular and humoral responses compared to s.c., i.d. and i.m. injection.
(a) Quantification of the frequencies of IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells in spleens on d 7 post immunization (p.i.) by intracellular IFN-γ staining. (b) Quantification of IFN-γ production from memory splenocytes at 5 weeks p.i. by in vitro restimulation assay. (c) Serum VACV-specific IgG determined by ELISA at the indicated time points p.i.. Each data point represents the average OD450nm value ± s.e.m. n = 5 in each group. (d) Serum VACV-specific IgG titer determined 11 weeks p.i.. n = 8–10 in each group. Data are representative results from 2–3 independent experiments. UI: unimmunized control.