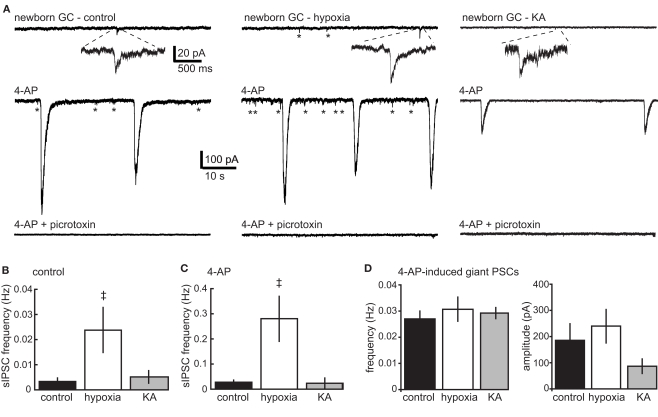
Figure 2.
Enhanced GABAergic input to newborn GCs after hypoxia but not KA treatment. (A) Current traces from newborn GCs in control, hypoxia-, and KA-treated mice recorded on P17.Top traces show spontaneous synaptic events during a control period in the absence of receptor antagonists. Addition of the K+ channel blocker 4-AP (100 μM; middle traces) increased the frequency of spontaneous events (asterisks) in GCs from control and hypoxia-treated mice, but not in GCs from KA-treated mice. 4-AP also triggered large compound events in GCs from all groups. All spontaneous synaptic currents were blocked by picrotoxin (bottom traces). (B,C) The frequency of spontaneous events was increased in newborn GCs from hypoxia-treated mice. The double dagger (‡) indicates significantly different from control (ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). The same results were obtained when cells with no detected events in the control condition were excluded from analysis (not shown). The frequency of spontaneous events was not increased in newborn GCs from KA-treated mice. (D) There was no difference in the frequency or amplitude of 4-AP-induced compound events (ANOVA, p = 0.18).