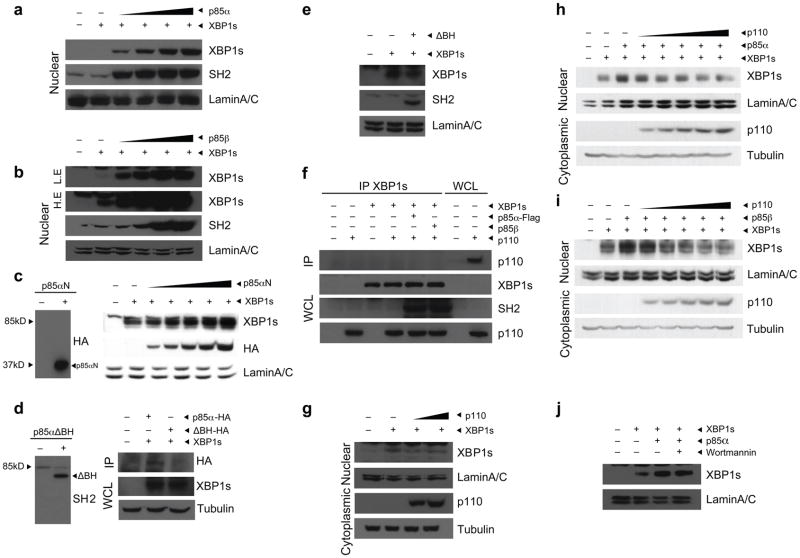
Figure 2.
p85α and p85β increase nuclear translocation of XBP-1s. (a,b) Nuclear protein amounts of XBP-1s and p85 in MEFs infected with Ad-XBP-1s and with increasing doses of Ad-p85α (a) or Ad-p85β (b). Lamin A/C was used as a control for nuclear protein level. (c) Left, western blot for HA in MEFs infected with p85αN-HA. Right, nuclear protein amounts of XBP-1s, p85αN-HA and lamin A/C in MEFs expressing XBP-1s together with increasing amounts of p85αN-HA. (d) Left, western blot for SH2 in MEFs infected with p85αΔBH-HA. Right, immunoblotting for HA in XBP-1 immunoprecipitates from MEFs infected with Ad-XBP-1s and with either p85α-HA or p85αΔBH-HA. (e) Immunoblotting of MEFs infected with Ad-XBP-1s or with Ad-XBP-1s and Ad-p85αΔBH-HA together. Nuclear proteins were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (f) Western blot for p110 in XBP-1 immunoprecipitates and for XBP-1s, SH2 and p110 in whole-cell lysates from cells infected with Ad-XBP-1s, Ad-p110, Ad-XBP-1s and Ad-p110, Ad-XBP-1s, Ad-p110 and Ad-p85α or Ad-XBP-1s, Ad-p110 and Ad-p85β. (g) XBP-1s and lamin A/C protein levels after infection of MEFs with a constant dose of Ad-XBP-1s and increasing doses of Ad-p110. (h,i) Nuclear protein amounts of XBP-1s and lamin A/C in cells infected with Ad-XBP-1s and Ad-p85α (h) or Ad-p85β (i) and with increasing doses of Ad-p110. (j) XBP-1s nuclear protein amounts in the presence or absence of wortmannin (100 μM). Experiments were independently repeated three times.