Abstract
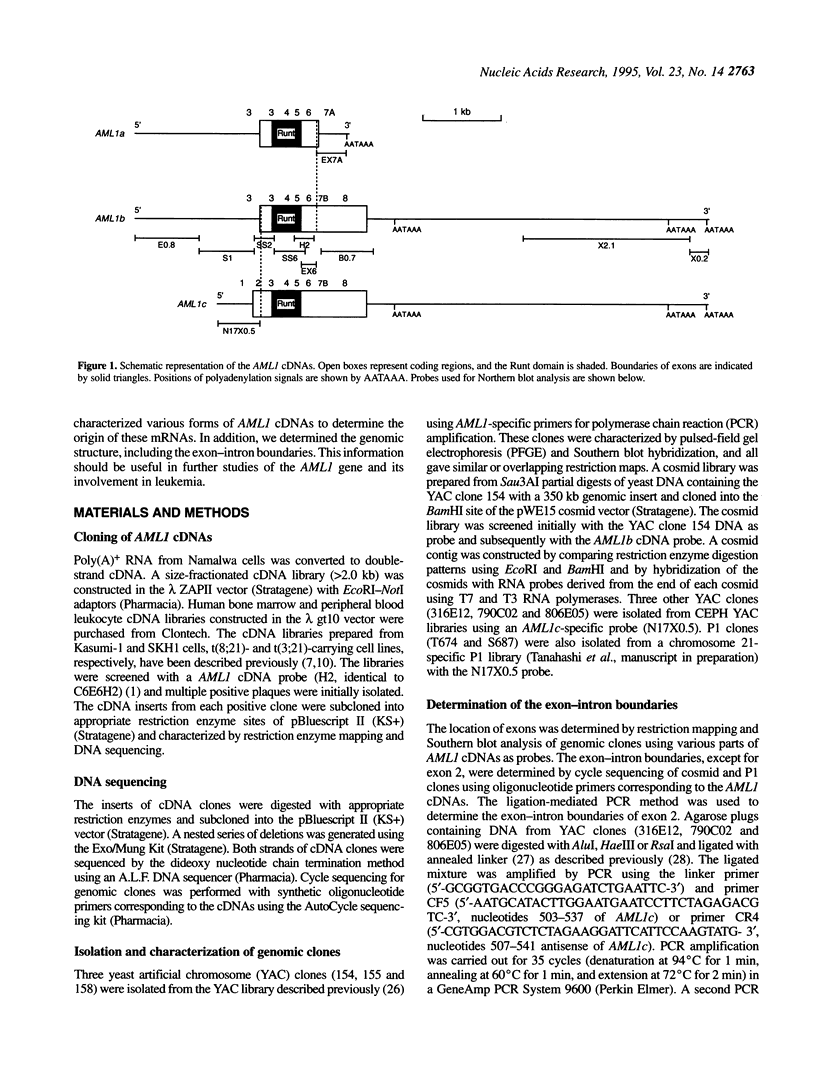
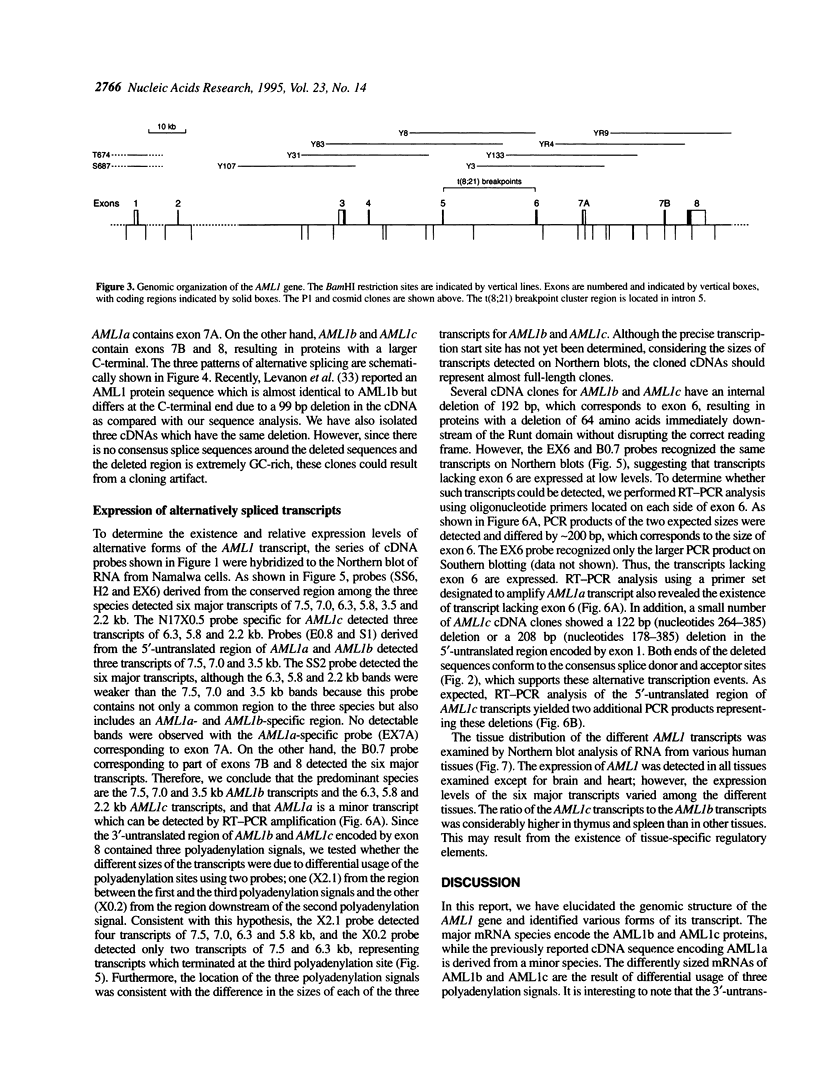
We previously isolated the AML1 gene, which is rearranged by the t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia. The AML1 gene is highly homologous to the Drosophila segmentation gene runt and the mouse transcription factor PEBP2 alpha subunit gene. This region of homology, called the Runt domain, is responsible for DNA-binding and protein--protein interaction. In this study, we isolated and characterized various forms of AML1 cDNAs which reflect a complex pattern of mRNA species. Analysis of these cDNAs has led to the identification of two distinct AML1 proteins, designated AML1b (453 amino acids) and AML1c (480 amino acids), which differ markedly from the previously reported AML1a (250 amino acids) with regard to their C-terminal regions, although all three contain the Runt domain. The large C-terminal region common to AML1b and AML1c is suggested to be a transcriptional activation domain. AML1c differs from AML1b by only 32 amino acids in the N-terminal. Characterization of the genomic structure revealed that the AML1 gene consists of nine exons and spans > 150 kb of genomic DNA. Northern blot analysis demonstrated the presence of six major transcripts, encoding AML1b or AML1c, which can all be explained by the existence of two promoters, alternative splicing and differential usage of three polyadenylation sites. A minor transcript encoding AML1a which results from alternative splicing of a separate exon can be detected only by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction amplification. The distinct proteins encoded by the AML1 gene may have different functions, which could contribute to regulating cell growth and/or differentiation through transcriptional regulation of a specific subset of target genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bae S. C., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Oka H., Satake M., Shigesada K., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Ito Y. PEBP2 alpha B/mouse AML1 consists of multiple isoforms that possess differential transactivation potentials. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3242–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Inuzuka M., Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. Isolation of PEBP2 alpha B cDNA representing the mouse homolog of human acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daga A., Tighe J. E., Calabi F. Leukaemia/Drosophila homology. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):484–484. doi: 10.1038/356484b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis I., Ish-Horowicz D. Apical localization of pair-rule transcripts requires 3' sequences and limits protein diffusion in the Drosophila blastoderm embryo. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):927–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90366-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt acts as a position-specific numerator element necessary for the uniform expression of the sex-determining gene Sex-lethal. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2176–2187. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. B., Kania M. A., Gergen J. P. Expression and function of the Drosophila gene runt in early stages of neural development. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1223–1230. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson P., Gao J., Chang K. S., Look T., Whisenant E., Raimondi S., Lasher R., Trujillo J., Rowley J., Drabkin H. Identification of breakpoints in t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia and isolation of a fusion transcript, AML1/ETO, with similarity to Drosophila segmentation gene, runt. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1825–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavis E. R., Lehmann R. Localization of nanos RNA controls embryonic polarity. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90358-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai T., Olson M. V. Second-generation approach to the construction of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y., Miyoshi H., Ohki M., Pepling M., Gergen P. The Runt domain identifies a new family of heteromeric transcriptional regulators. Trends Genet. 1993 Oct;9(10):338–341. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90026-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Ogawa E., Asano M., Ishida S., Murakami Y., Satake M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Purification of a mouse nuclear factor that binds to both the A and B cores of the polyomavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4808–4819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4808-4819.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania M. A., Bonner A. S., Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt encodes a novel nuclear regulatory protein that is also expressed in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1701–1713. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kere J., Nagaraja R., Mumm S., Ciccodicola A., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Mapping human chromosomes by walking with sequence-tagged sites from end fragments of yeast artificial chromosome inserts. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozu T., Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Asou H., Kamada N., Ohki M. Junctions of the AML1/MTG8(ETO) fusion are constant in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1270–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagnado C. A., Brown C. Y., Goodall G. J. AUUUA is not sufficient to promote poly(A) shortening and degradation of an mRNA: the functional sequence within AU-rich elements may be UUAUUUA(U/A)(U/A). Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):7984–7995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.7984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Negreanu V., Bernstein Y., Bar-Am I., Avivi L., Groner Y. AML1, AML2, and AML3, the human members of the runt domain gene-family: cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal localization. Genomics. 1994 Sep 15;23(2):425–432. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Tarlé S. A., Hajra A., Claxton D. F., Marlton P., Freedman M., Siciliano M. J., Collins F. S. Fusion between transcription factor CBF beta/PEBP2 beta and a myosin heavy chain in acute myeloid leukemia. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1041–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.8351518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. cis-acting sequences responsible for anterior localization of bicoid mRNA in Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):595–598. doi: 10.1038/336595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maseki N., Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Homma C., Ohki M., Sakurai M., Kaneko Y. The 8;21 chromosome translocation in acute myeloid leukemia is always detectable by molecular analysis using AML1. Blood. 1993 Mar 15;81(6):1573–1579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Downing J. R., Hiebert S. W. Identification of AML-1 and the (8;21) translocation protein (AML-1/ETO) as sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins: the runt homology domain is required for DNA binding and protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6336–6345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani K., Ogawa S., Tanaka T., Miyoshi H., Kurokawa M., Mano H., Yazaki Y., Ohki M., Hirai H. Generation of the AML1-EVI-1 fusion gene in the t(3;21)(q26;q22) causes blastic crisis in chronic myelocytic leukemia. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):504–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Kozu T., Shimizu K., Enomoto K., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Kamada N., Ohki M. The t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia results in production of an AML1-MTG8 fusion transcript. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2715–2721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Kozu T., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Ohki M. t(8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10431–10434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry K. L., Melton D. A. Vegetal messenger RNA localization directed by a 340-nt RNA sequence element in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):991–994. doi: 10.1126/science.1546297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchprayoon I., Meyers S., Scott L. M., Suzow J., Hiebert S., Friedman A. D. PEBP2/CBF, the murine homolog of the human myeloid AML1 and PEBP2 beta/CBF beta proto-oncoproteins, regulates the murine myeloperoxidase and neutrophil elastase genes in immature myeloid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5558–5568. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Begy C. R., Erickson P., Drabkin H. A., Rowley J. D. The 3;21 translocation in myelodysplasia results in a fusion transcript between the AML1 gene and the gene for EAP, a highly conserved protein associated with the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7784–7788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Begy C. R., Kobayashi H., Roulston D., Claxton D., Pedersen-Bjergaard J., Parganas E., Ihle J. N., Rowley J. D. Consistent intergenic splicing and production of multiple transcripts between AML1 at 21q22 and unrelated genes at 3q26 in (3;21)(q26;q22) translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4004–4008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Birn D. J., Erickson P., Gao J., LeBeau M. M., Drabkin H. A., Rowley J. D. Detection of DNA rearrangements in the AML1 and ETO loci and of an AML1/ETO fusion mRNA in patients with t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1993 Feb 15;81(4):883–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Birn D. J., Espinosa R., 3rd, Erickson P., LeBeau M. M., Roulston D., McKeithan T. W., Drabkin H., Rowley J. D. Involvement of the AML1 gene in the t(3;21) in therapy-related leukemia and in chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis. Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2728–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Inuzuka M., Maruyama M., Satake M., Naito-Fujimoto M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEBP2 beta, the heterodimeric partner of a novel Drosophila runt-related DNA binding protein PEBP2 alpha. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):314–331. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Kagoshima H., Inuzuka M., Lu J., Satake M., Shigesada K., Ito Y. PEBP2/PEA2 represents a family of transcription factors homologous to the products of the Drosophila runt gene and the human AML1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6859–6863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Blau H. M. Genetic complementation reveals a novel regulatory role for 3' untranslated regions in growth and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):903–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90579-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Inuzuka M., Shigesada K., Oikawa T., Ito Y. Differential expression of subspecies of polyomavirus and murine leukemia virus enhancer core binding protein, PEBP2, in various hematopoietic cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):714–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Nomura S., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Takahama Y., Hashimoto Y., Niki M., Kitamura Y., Ito Y. Expression of the Runt domain-encoding PEBP2 alpha genes in T cells during thymic development. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1662–1670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Miyoshi H., Kozu T., Nagata J., Enomoto K., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Ohki M. Consistent disruption of the AML1 gene occurs within a single intron in the t(8;21) chromosomal translocation. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6945–6948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirito M., Lin Q., Maity T., Sawadogo M. Ubiquitous expression of the 43- and 44-kDa forms of transcription factor USF in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):427–433. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzow J., Friedman A. D. The murine myeloperoxidase promoter contains several functional elements, one of which binds a cell type-restricted transcription factor, myeloid nuclear factor 1 (MyNF1). Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2141–2151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Tanaka K., Ogawa S., Kurokawa M., Mitani K., Nishida J., Shibata Y., Yazaki Y., Hirai H. An acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1, regulates hemopoietic myeloid cell differentiation and transcriptional activation antagonistically by two alternative spliced forms. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):341–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tighe J. E., Daga A., Calabi F. Translocation breakpoints are clustered on both chromosome 8 and chromosome 21 in the t(8;21) of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1993 Feb 1;81(3):592–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Wang Q., Crute B. E., Melnikova I. N., Keller S. R., Speck N. A. Cloning and characterization of subunits of the T-cell receptor and murine leukemia virus enhancer core-binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3324–3339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Struhl G. RNA regulatory elements mediate control of Drosophila body pattern by the posterior morphogen nanos. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):955–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Fujioka K., Hetherington C. J., Shapiro L. H., Chen H. M., Look A. T., Tenen D. G. Identification of a region which directs the monocytic activity of the colony-stimulating factor 1 (macrophage colony-stimulating factor) receptor promoter and binds PEBP2/CBF (AML1). Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8085–8095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Yeadon J. E., Burden S. J. AML1 is expressed in skeletal muscle and is regulated by innervation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8051–8057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]