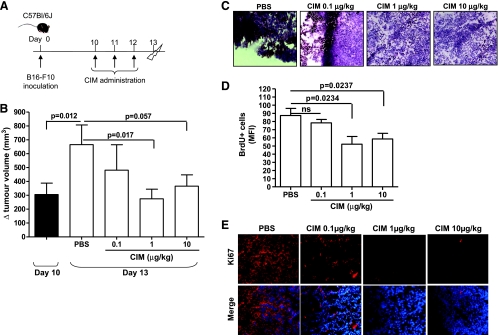
Figure 1.
CIM inhibits tumor growth in melanoma-bearing mice. (A) Experimental protocol: 10 days after B16-F10 cell implantation, C57Bl/6 mice were treated (i.p.) with CIM (0.1-1-10 µg/kg) or PBS on days 10, 11, and 12, and mice were killed on day 13. (B) Tumor volume was measured at days 10 and 13 and plotted as volume increase (Δ mm3). At day 10, the tumor volume was 305.4 ± 82.48 mm3. The tumor volume significantly increased between days 10 and 13 in PBS-treated mice. Administration of CIM significantly reduced tumor volume compared with PBS (n = 20). Reduced cell proliferation was observed in CIM-treated mice as determined by representative H&E staining of melanoma tissue-derived cryosections (magnification, x20; C), by reduced numbers of BrdU+ cells (D), and by Ki67 by immunofluorescence staining (magnification, x40; E). ns indicates not significant. Data shown are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett post hoc analysis.