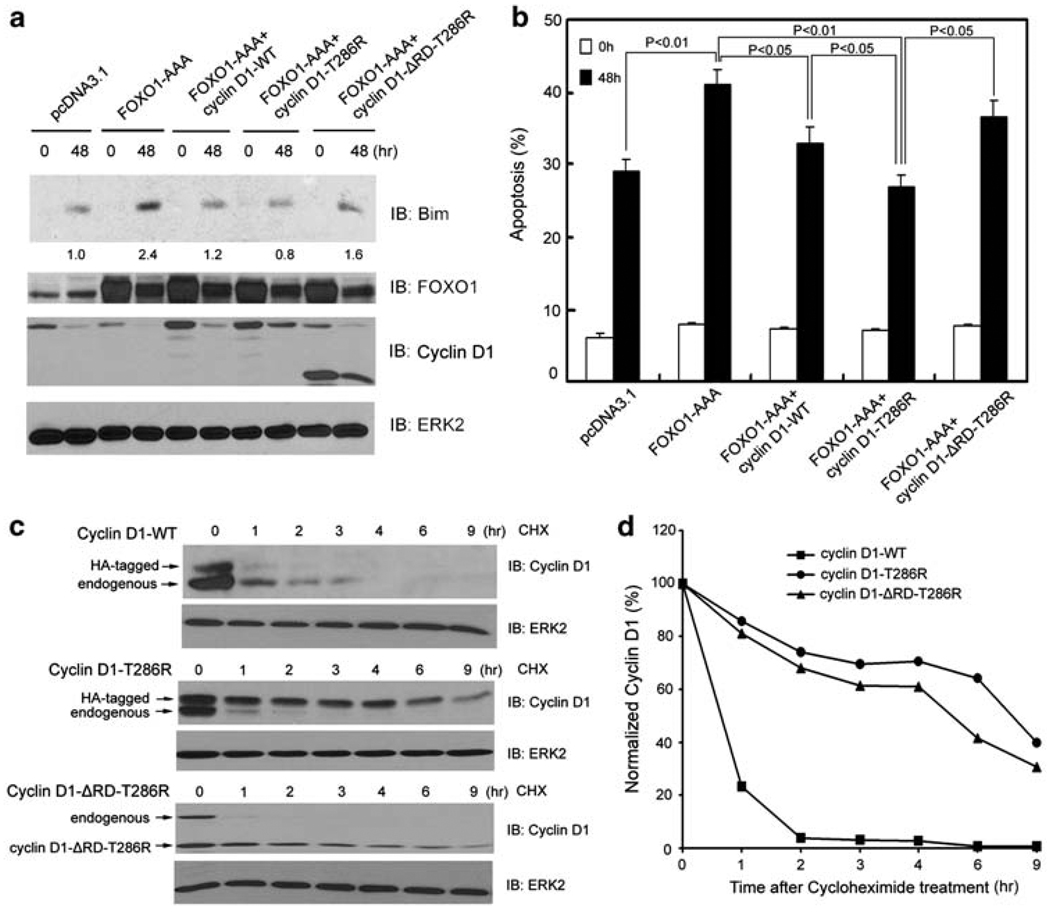
Figure 5.
Inhibitory effect on FOXO1-mediated anoikis and protein stability of wild type and a cancer-derived mutant of cyclin D1. (a, b) DU145 cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. At 24 h after transfection, cells were cultured in suspension and at the indicated time points cells were subjected to immunoblotting (a) and apoptosis (b) analysis. The number underneath each band in the immunoblot indicates the relative intensity of the corresponding band. (c) DU145 cells were transfected with HA-tagged wild-type cyclin D1, HA-tagged cyclin D1-T286R, or cyclin D1-ΔRD-T286R mutants. At 48 h after transfection, DU145 cells were cultured in suspension and treated with 20 µg/ ml cycloheximide. Cells were collected at the indicated time points and cell lysates were analyzed by western blots. (d) Quantification of the cyclin D1 protein signal intensity was obtained from exposures in which the signal was not saturated during the entire time course. Signal intensities were normalized to the signal intensity obtained at time zero