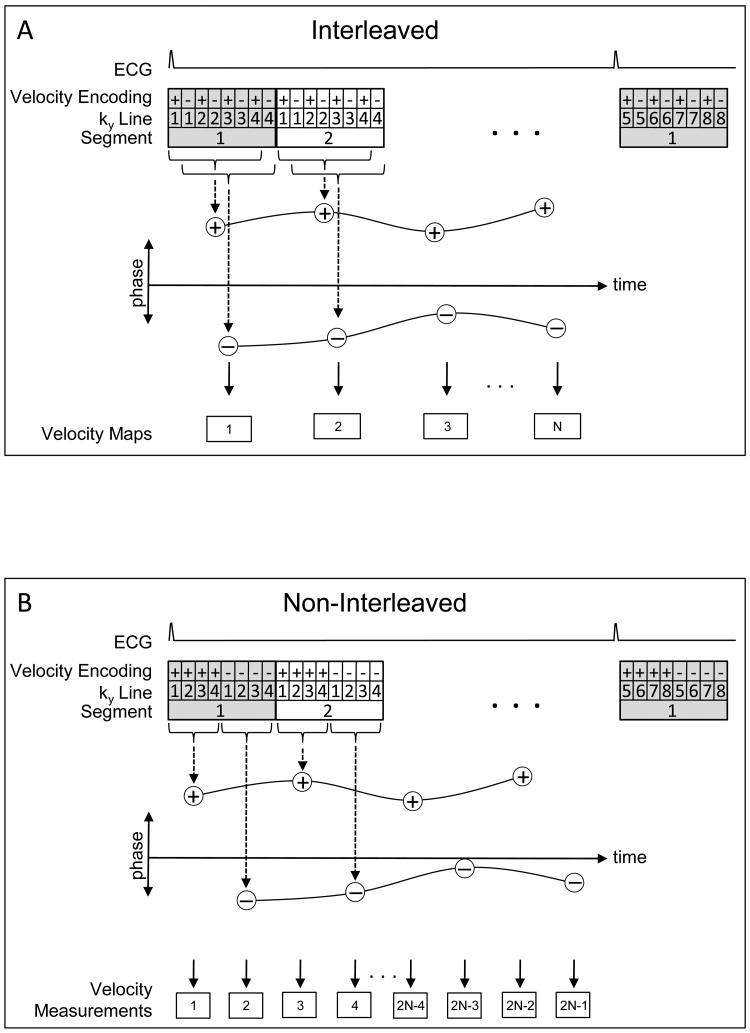
Figure 1.
Comparison of the acquisition strategies for the interleaved (A) and non-interleaved (B) velocity encoding phase-contrast techniques. (A) Temporal window for each velocity/magnitude pair is 7 TRs (time to collect all positive or all negative encodings) with a 1TR offset between positively and negatively velocity encoded images, providing velocity measurements every 8 TRs. (B) Temporal window for each image is 4 TRs with a 4TR offset between positively and negatively velocity encoded images, which, with appropriate processing of ROIs, produces velocity measurements every 4 TRs. Phase-difference is derived from subtracting spline curves fit between the two sets of data points.