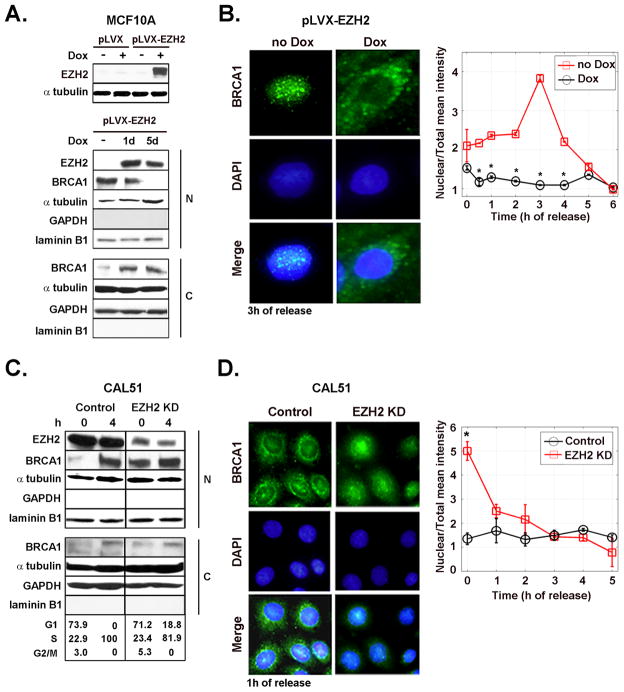
Figure 1. EZH2-dependent regulation of BRCA1 intracellular localization.
A. Inducible synthesis of EZH2 in MCF10A cells and its effect on BRCA1 protein. Western blot analysis of MCF10A cells transduced with the empty vector (pLVX) and with EZH2-containing vector (pLVX-EZH2). Cells were untreated or treated with Dox (500 ng/ml) to induce EZH2 expression. Underneath is a Western blot of EZH2 and BRCA1 proteins in nuclear and cytoplasmic enriched fractions of pLVX-EZH2 cells untreated or treated with Dox. Laminin B1 and GAPDH confirm nuclear and cytoplasmic enrichment of the fractionated samples, respectively. B. Effect of EZH2 overexpression on the intracellular localization of BRCA1 protein. Representative immunofluorescence images of BRCA1 protein at 3 h after release of G1/S cell cycle block (double thymidine block). The graph shows the mean intensity of BRCA1 protein expression in the nucleus normalized to the total intensity at different times after release from cell cycle block. The percentage of cells in each cell cycle phase after release of cell cycle block for untreated and Dox treated cells was at 0 h: G1 94.84%, S 5.15%, G2/M 0%, and G1 94.09%; S 4.97%, G2/M 0.94%, respectively. At 4 h: G1 78.52%, S 21.02%, G2/M 0.46%, and G1 74.27%, S 25.7%, G2/M 0.03%, respectively. C. Western blot for EZH2 and BRCA1 proteins in CAL51/EZH2 KD and controls at 0 and 4 h after release of cell cycle block. The number of cells in G1, S and M cell cycle phases was obtained by flow cytometry. D. Representative immunofluorescence images of BRCA1 protein at 1 h after release of cell cycle block and quantification of results, as described above. The experiment was repeated for three independent times. Error bars are the standard deviation and * represents p<0.05.