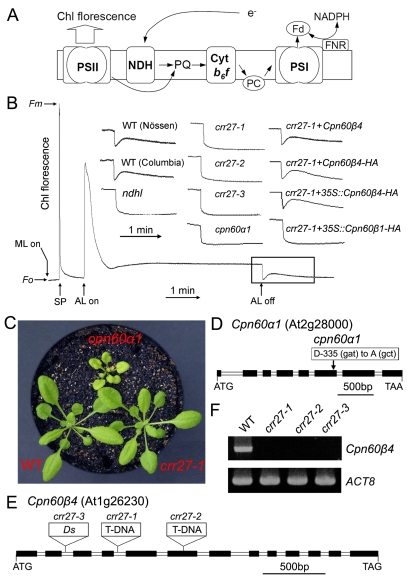
Figure 1. Characterization of cpn60α1 and crr27 mutants.
(A) A schematic model of NDH function. The NDH complex mediates electron transfer from the stromal reducing pool to plastoquinone (PQ). PQ reduction in the dark depends on NDH activity and can be detected by the transient rise of chlorophyll (Chl) fluorescence after illumination with actinic light (AL). For simplicity, this model does not include the information that NDH interacts with PSI. Cyt, cytochrome; PC, plastocyanin; Fd, ferredoxin. (B) Determination of NDH activity using Chl fluorescence analysis. The bottom curve indicates a typical trace of Chl fluorescence in the WT plants. Leaves were exposed to AL for 5 min. AL was turned off and the subsequent transient rise in fluorescence ascribed to NDH activity was monitored using a PAM Chl fluorometer. Insets are magnified traces from the boxed area. crr27-1+Cpn60β4 and crr27-1+Cpn60β4-HA represent crr27-1 transformed by the WT genomic Cpn60β4 and genomic Cpn60β4 fused to the HA epitope-tag, respectively. crr27-1+35S::Cpn60β4-HA and crr27-1+35S::Cpn60β1-HA represent crr27-1 transformed with Cpn60β4 and Cpn60β1 cDNA, respectively, fused to the sequence encoding the HA-tag expressed under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. Fluorescence levels were standardized to the maximum fluorescence levels of closed PSII (Fm) by applying saturating-light pulses (SP). ML, measuring light; Fo, minimum fluorescence level of open PSII. (C) Visible phenotype of mutants. Seedlings were cultured at 50 µmol photons m−2 s−1 for 4 wk after germination. (D and E) Mutations in cpn60α1 (D) and three crr27 mutant alleles (E) are indicated. (F) RT-PCR analysis of the Cpn60β4 transcript in WT and crr27 mutants. ACT8 was used as a control.