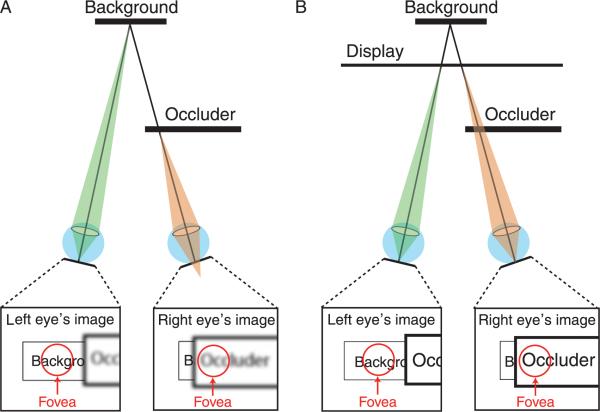
Figure 10.
Monocular occlusions in natural viewing and with conventional stereo displays. A) Natural viewing. An opaque surface monocularly occludes a more distant background surface. The eyes are converged and focused on the background. The insets represent the retinal images for this viewing situation. The background is visible on the fovea of the left eye but not on the fovea of the right eye. The retinal image of the background is well focused and the image of the occluder is not. B) The same viewing situation presented in a conventional stereo display. The eyes are converged at the simulated distance of the background, but they are focused at the surface of the display because the light comes from there. The insets again represent the retinal images for this viewing situation. The retinal images of the background and occluder are well focused.