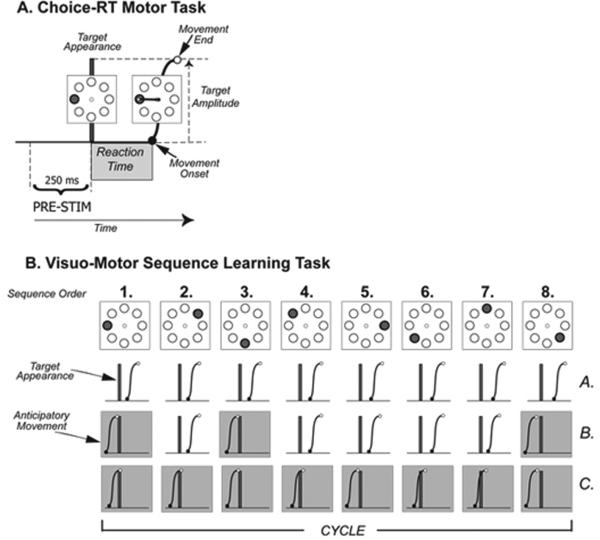
Figure 1.
A - The time line for a single trial of the choice RT motor task with representation of the target array. B – Schematic illustration of the development of anticipatory movements during sequence learning. Target are presented at constant time interval of 1.5 s so that temporal occurrence is predictable. At the beginning (A.) movements initiate after target appearance in the course of learning; (B>) movements start becoming anticipatory (grey boxed hand path). Finally, when the sequence is entirely known (C.), all the target appearances are anticipated.