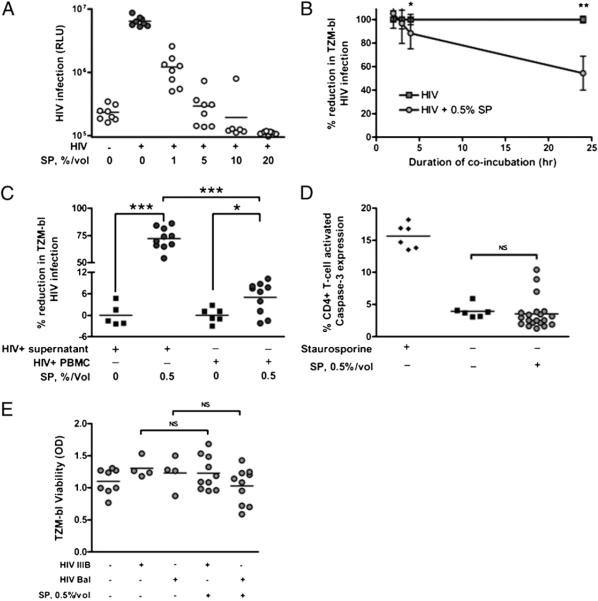
FIGURE 4.
Magnitude of protection of CD4+ target cells from HIV infection by SP is influenced by SP concentration, incubation duration, and cell contact, but not by target cell apoptosis. Incubation with higher concentrations of SP conferred greater CD4+ TZM-bl cell protection from HIV IIIB infection at an MOI of 0.2 (A, n = 8). Incubation with SP for greater than 2 h was associated with greater protection of CD4+ TZM-bl cells from infection with HIV BaL (B, n = 8). SP inhibits both cell-associated and cell-free HIV IIIB infection of TZM-bl cells, but the magnitude of SP inhibition of cell-associated HIV infection of TZM-bl cells was smaller than the magnitude of SP inhibition of cell-free HIV infection of TZM-bl cells (C, n = 10). Incubation with 0.5% SP for 24 h did not induce CD4+ T cell apoptosis as measured by intracellular expression of activated caspase-3 (D, n = 20) or by MTT viability assay in TZM-bl cells (E, n = 10). Staurosporine 0.25 μM was used as a positive control for intracellular activated caspase-3 expression. Error bars depict SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. RLU, relative light units.