Figure 3.
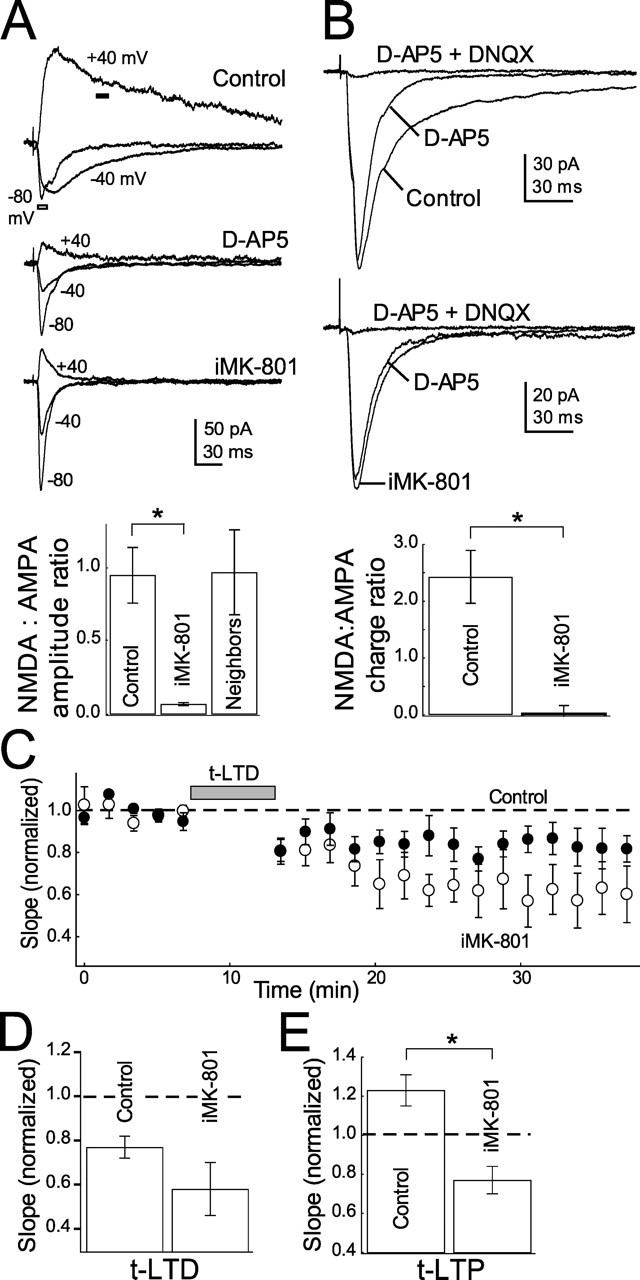
Blockade of postsynaptic NMDA currents by internal MK-801 does not block t-LTD. A, iMK-801 (1 mm) substantially blocks NMDA currents measured at +40 mV. Top, Representative EPSCs measured in control cells and in the presence of 50 μm d-AP5 and 1 mm internal MK-801. Holding potentials are indicated. Bottom, Quantification of NMDA (amplitude of current at +40 mV at dark bar in A1) to AMPA (amplitude of current at −80 mV at outlined bar in A) current ratios in control, d-AP5, iMK-801 conditions and cells recorded with normal internal within 10 μm of cells recorded with iMK-801 (neighbors). B, iMK-801 also blocks NMDA currents at −60 mV. Top, Representative EPSCs recorded at −60 mV in low (0.4 mm) Mg2+ Ringer’s solution in control (top) and MK-801 (bottom) internals in normal Ringer’s solution, 50 μm d-AP5 and 10 μm DNQX. Bottom, Quantification of the NMDA:AMPA current integral ratio (see Materials and Methods) for all cells tested. C, iMK-801 does not block t-LTD. The net effect of iMK-801 on t-LTD is plotted with interleaved controls. Open circles, iMK-801; closed circles, interleaved controls. D, Summary of the effect of iMK-801 on t-LTD. E, iMK-801 does block t-LTP. Error bars show mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.
