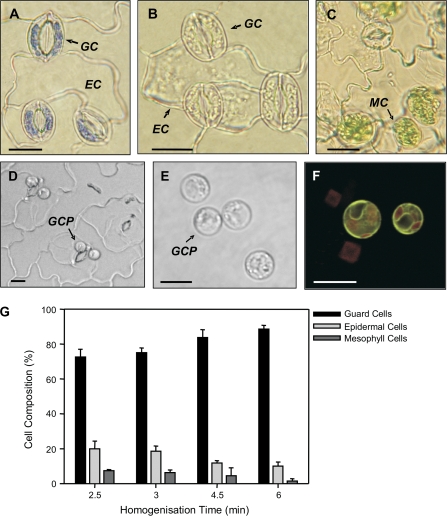
Fig. 5.
Guard cells isolated via the epidermal fragmentation method (A–C). Guard cells (GC) were considered viable on the basis of being able to take up and retain toluidine blue but neighbouring epidermal cells (EC) lacking cytoplasm did not retain the stain (A). EC and mesophyll cell (MC) were observed in all fragment preparations (B, C). GCPs were isolated following the method of Leonhardt et al. (2004) (D, E). Following release of GCPs from intact, purified epidermal fragments (D), the GCPs comprised approximately 90% of the cell population (E). (F) The cellular identity of protoplasts was confirmed by confocal microscopy of samples from the guard cell-specific enhancer trap line E1728. (G) Determination of the cellular composition of epidermal fragments with increasing homogenization times. For all cell counts, 500 cells were examined in three independent replicates. The contribution of vascular tissue could not be determined and is therefore not represented. Scale bars in (A)–(F) represent 15 μm.