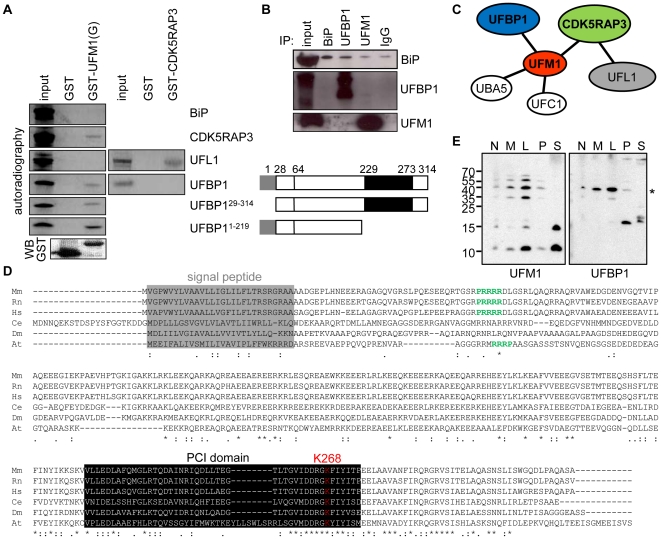
Figure 2. UFM1 interacts with UFBP1 and CDK5RAP3.
A GST pull down (UFM1(G) and CDK5RAP3) with in vitro T7 transcribed/translated 35S-labelled UFBP1, UFBP129–314, UFBP11–219 CDK5RAP3, UFL1 and BiP. Lane 1 shows the starting labeled proteins used for the pull down experiment (input) and a schematic overview of the used UFBP1 constructs. A GST-antibody was used for immunoblotting (WB), B co-immunoprecipitation with BiP, UFL1 and UFM1 specific antibodies, C Schematic overview of the protein interactions of UFM1 demonstrated in mouse in this manuscript, D Evolutionary conservation of UFBP1 (2600009E05Rik). Protein sequence in Mm (Musmusculus), Rn (Rattusnovergicus), Hs (Homo sapiens), Dr (Daniorerio), Gg (Gallus gallus), Tn (Tetraodonnigroviridis), Fr (Fuguribripes), Ag (Anopheles gambiae), Ce (Caenorhabditiselegans), Dm (Drosophila melanogaster) and At (Arabidopsis thaliana). Alignment was performed using ClustalW. The signal peptide of UFBP1 is boxed in grey, the nuclear localization signal is depicted in green, the PCI domain is boxed in black and lysine268 (K268) is shown in red, E Presence of UFM1 conjugates at the same height and with the same cellular localization as UFBP1 (*). MIN6 cell lysates were separated in 5 different fractions: N = nuclear and whole cell fraction (770×g), M = heavy mitochondrial fraction (2330×g), L = light mitochondrial, peroxisomal and lysosomal fraction (13,000×g), P = cell membrane fraction (100,000×g) and S = cytosolic and large protein complexes supernatant (100,000×g).