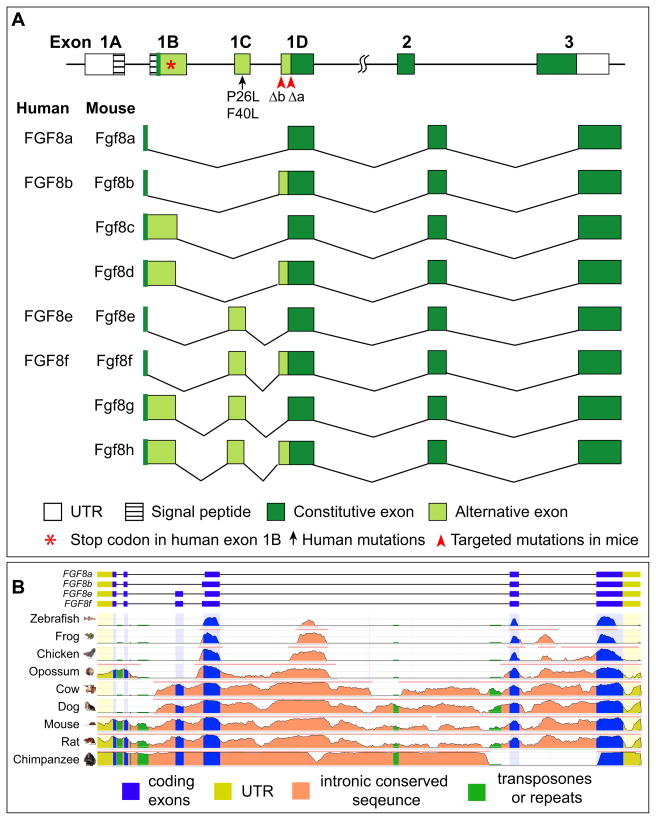
Figure 1.
(A) Genomic structure and different splice variants of the FGF8 gene in humans and mice. In humans, there is a stop codon (asterisk) in the exon 1B. Therefore, only four potential splice variants of human FGF8 instead of eight in mice. Targeted point mutations Δa and Δb (arrowheads) disrupt the splice acceptor in exon 1D abolishing Fgf8a-containing (a, c, e, and g) and Fgf8b-containing (b, d, f, and h) splice variants in mice. Missense mutations (arrow) have been identified in FGF8 exon 1C, which is only included in FGF8e and FGF8f, in patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. (B) Genome comparison of Fgf8 genes in different species. Note that the first four exons are highly diverse while the last two exons are conserved. Exons 1C is missing in zebrafihs, frog, chicken and opossum.