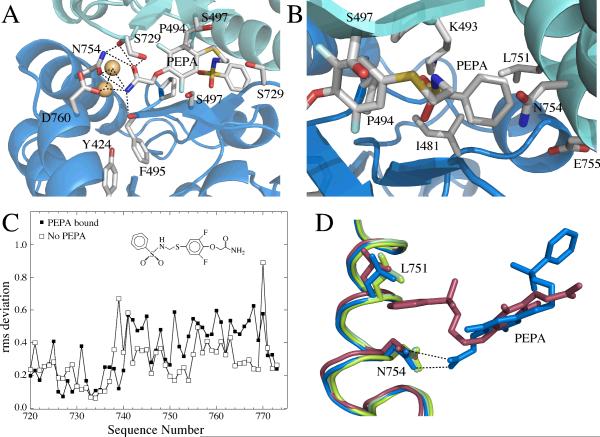
Figure 2.
The PEPA binding site, emphasizing the important interactions, shown in two orientations. (A) A view of the amide side of PEPA bound to GluA2 S1S2. The hydrogen bonding network with the amide of PEPA is shown as dotted lines. The H-bond with the sidechain of S729 is difficult to display in the orientation used in the figure. (B) A view of the phenyl group of PEPA inserted into a hydrophobic pocket in GluA2 S1S2. (C) RMS plot showing more variability in the J/K helices for the PEPA-bound structure than the unbound structure. (D) J/K helix showing where differences in the two orientations were analyzed. The amide of PEPA-N754 interaction (blue) maintains the position of the J helix in the absence of PEPA (green) The J helix is displaced on the phenyl side of PEPA (red).