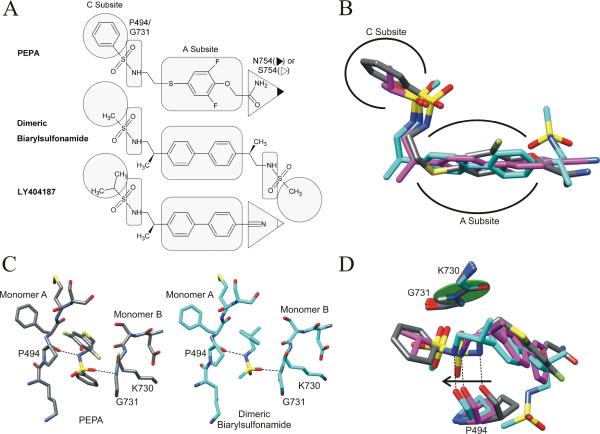
Figure 4.
(A) Members of the full spanning class of allosteric modulators. The shape-highlighted regions of the modulators illuminate key contact points to the specific binding pocket residues and subsites (as labeled for PEPA). (B) Overlay of the full spanning modulator structures. The structures were aligned at both sets of P494 and G731 residues. PEPA (gray) occupies a similar arrangement of subsites as the dimeric biarylsulfonamide (PDB entry 3bbr, cyan, 30) and LY404187 (PDB entry 3kgc, magenta, 8). (C) The sulfonamide bridges the two monomers in both PEPA and the dimeric biarylsulfonamide with the same interactions to P494 and G731. (D) The hydrogen bond between the carbonyl of P494 and the sulfonamide is maintained when the modulator is in a shifted position relative to the peptide plane of K730 and G731 (green disk) located on the opposite monomer.