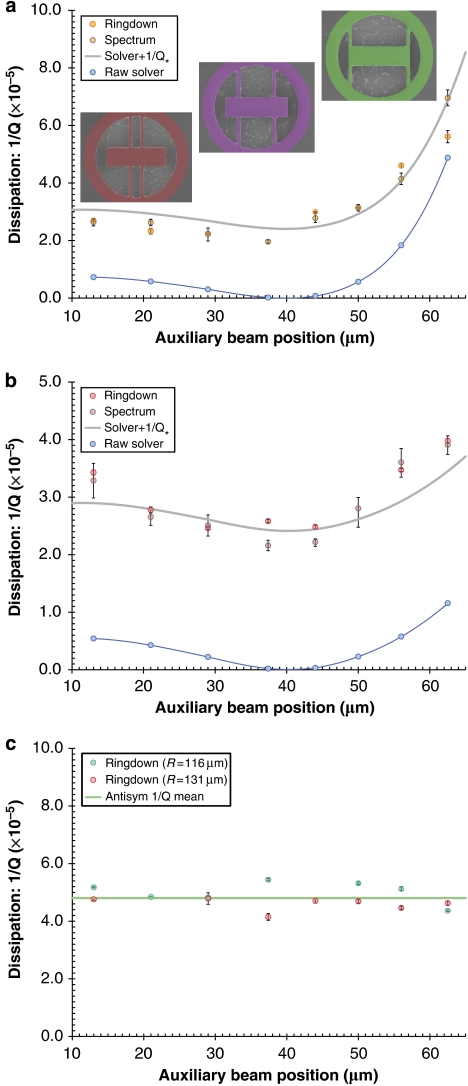
Figure 3. Compiled dissipation results displaying excellent agreement between the theory and experiment.
(a,b) Comparison of experimental measurements at T=20 K, with theoretical dissipation values for the free–free mode of resonators with measured central dimensions of 132×42 μm and radius R=116 μm and R=131 μm, respectively. Panel (a) includes SEM images of the three extreme designs (for R=116 μm) with overlaid CAD models of the resonator geometry. Both ringdown and spectrally-derived data are included, with values averaged over two nominally identical chips (error bars denote a confidence interval of 99%). We include both raw simulated data as well as fitted data (continuous lines are a guide to the eye) incorporating a constant offset 1/Q*=2.41×10−5. For the effective substrate, we utilize the mechanical properties of Ti, which is the main constituent of the positioning system on which the chips are mounted (ρ=4,540 kg m−3, Es=116 GPa and νs=0.34). (c) Measured dissipation for the antisymmetric (antisym) mode of the same structures exhibiting a lack of geometric dependence.