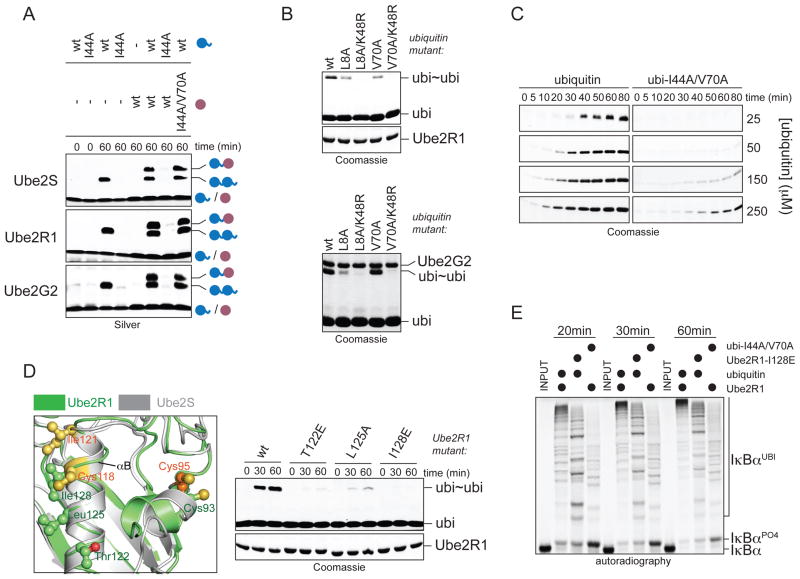
Figure 5. Non-covalent donor-binding is utilized by E2s independently of linkage specificity.
A. Ube2R1 and Ube2G2 require the hydrophobic patch in the donor, but not acceptor ubiquitin, for K48-linkage formation. Ube2S, Ube2R1, or Ube2G2 and its E3 gp78, were incubated with ubiΔGG or ubiΔGG/I44A/V70A (purple) and ubiquitin or ubiI44A (blue). Reactions were analyzed by Silver staining. B. The hydrophobic patch of donor ubiquitin is not required for K48-specificity of Ube2R1 or Ube2G2. ubi2-formation by Ube2R1 or Ube2G2/gp78 with ubiquitin mutants was analyzed by Coomassie staining. C. Donor-binding is required for rapid catalysis by Ube2R1. Time courses of ubi2-formation by Ube2R1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of ubiquitin or ubiI44A were analyzed by Coomassie staining. D. A similar surface as the donor-binding interface of Ube2S (grey) is required in Ube2R1 (green; PDB ID: 2OB4). Ube2R1 mutants were analyzed for K48-specific ubi2-formation by Coomassie staining. E. Donor-binding is required for processive chain formation by SCFβTrCP and Ube2R1. Phosphorylated IκBα was incubated with SCFβTrCP, Ube2R1 or Ube2R1I128E, and ubiquitin or ubiI44A/V70A and analyzed by autoradiography.